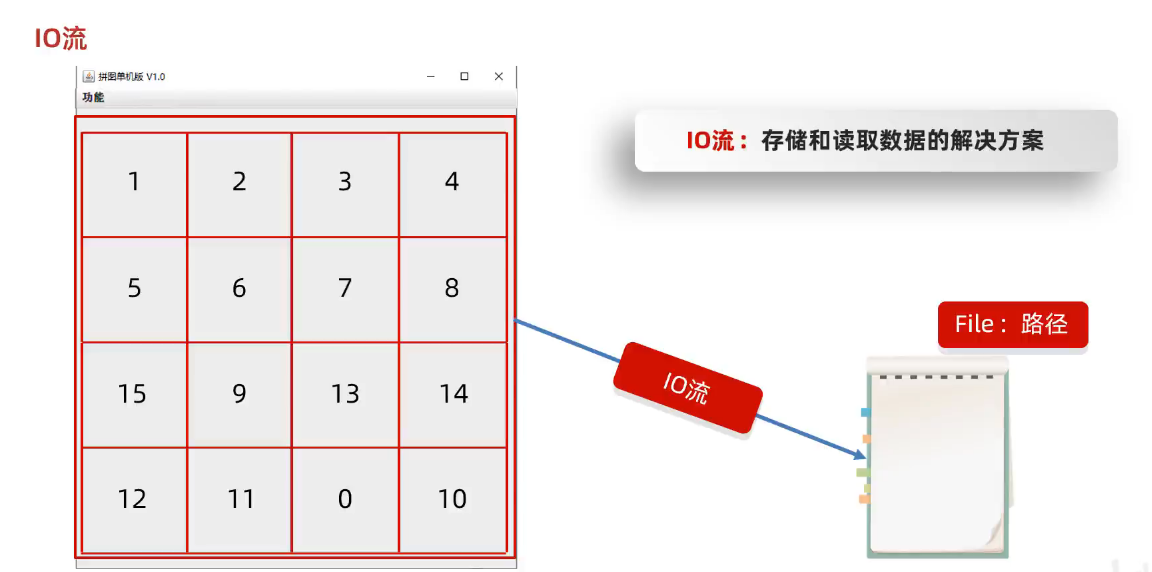
IO流
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
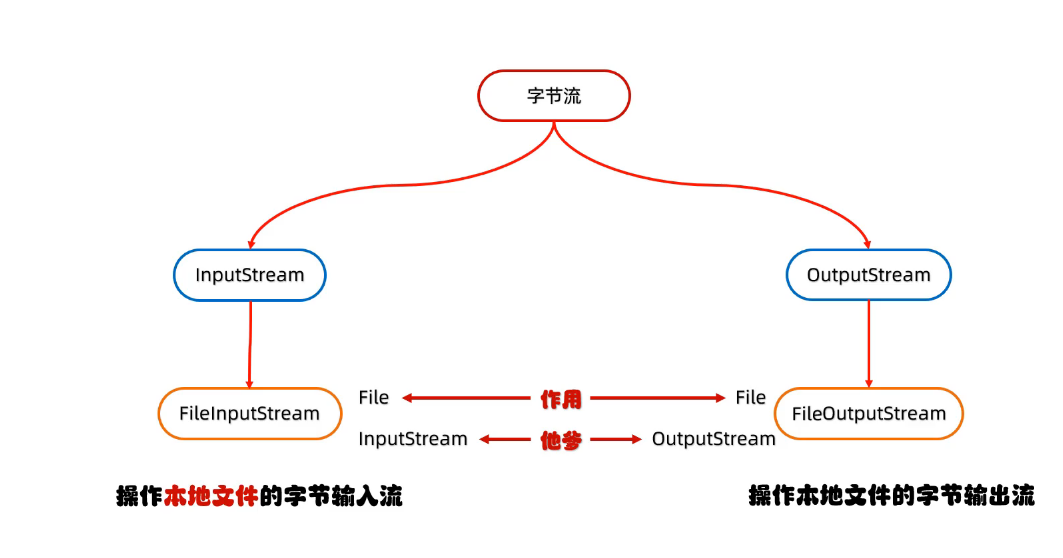
一、IO流的概述
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、什么是IO流
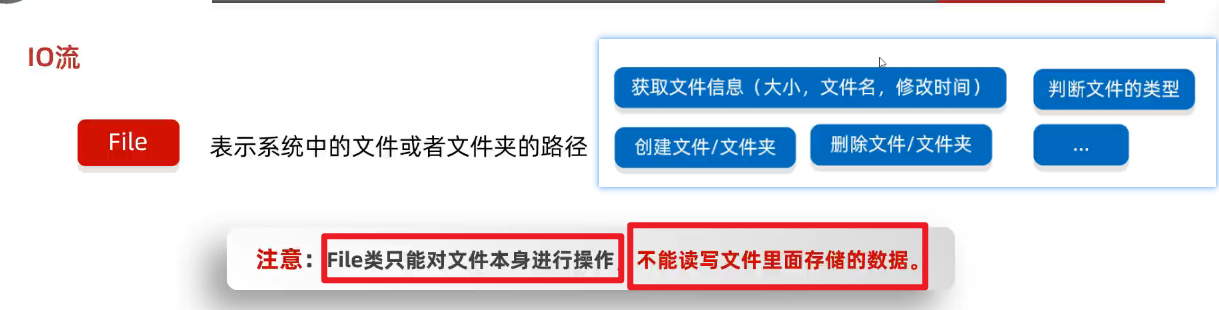
(1)File和IO的区别
(2)IO读写参照物-程序

- 以程序为参照物看读写方向也可以说以内存为参照物,因为程序是在内存中运行的
2、IO流的作用

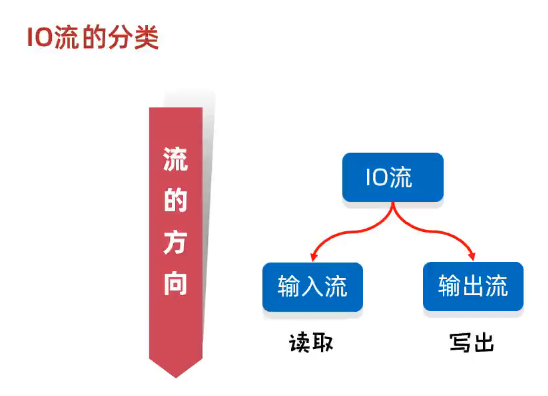
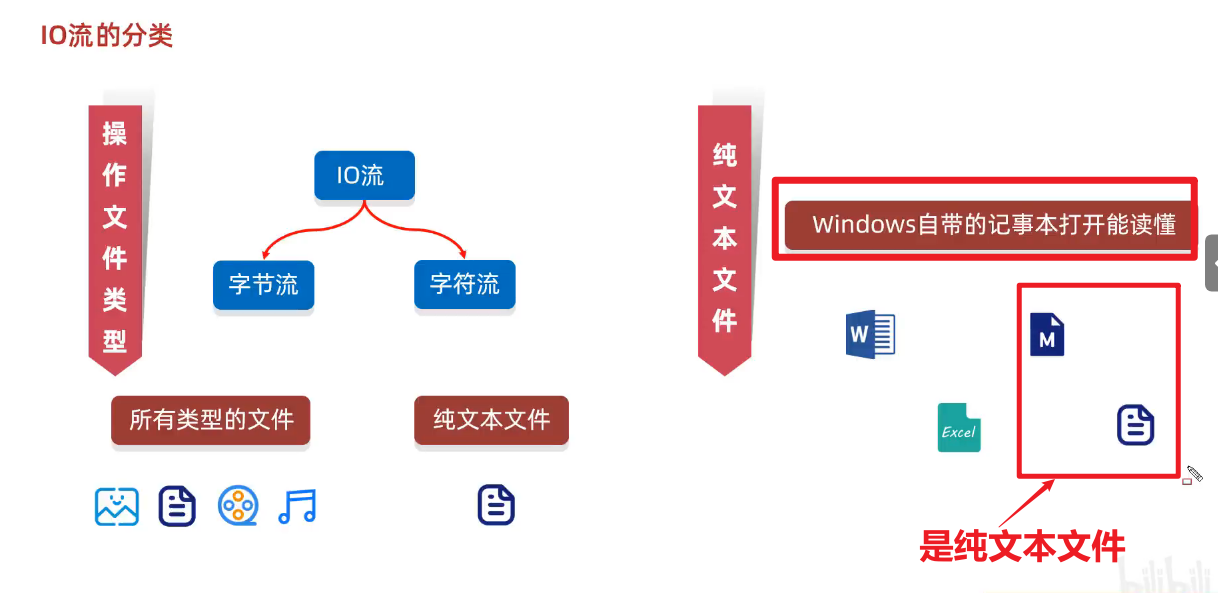
3、IO流的分类
(1)输入,输出流-按照==流向分类==
(2)字节,字符流-按照==操作文件的类型==分类
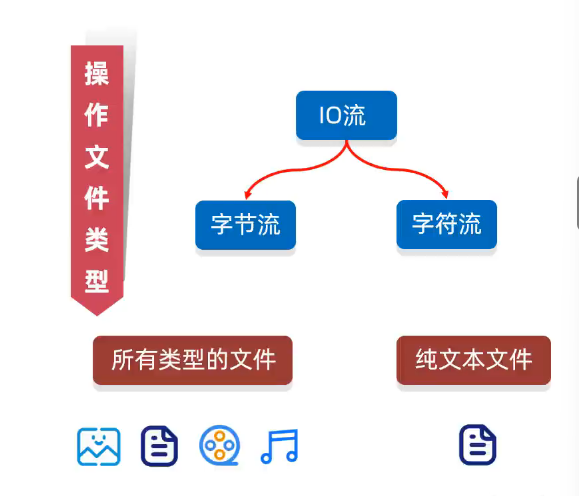
4、什么是纯文本文件
6、小结
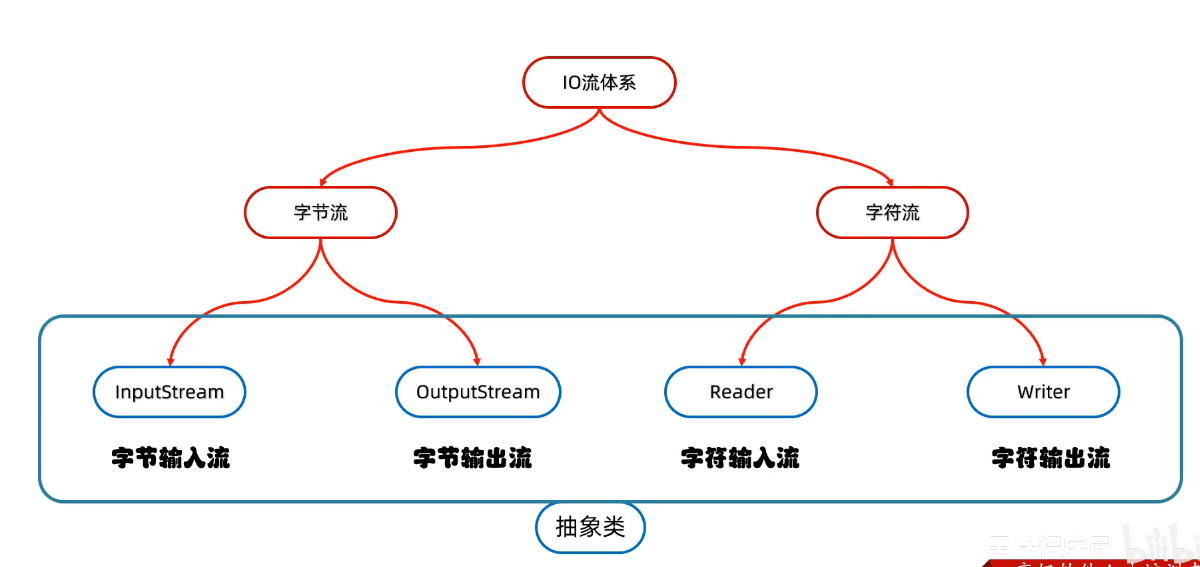
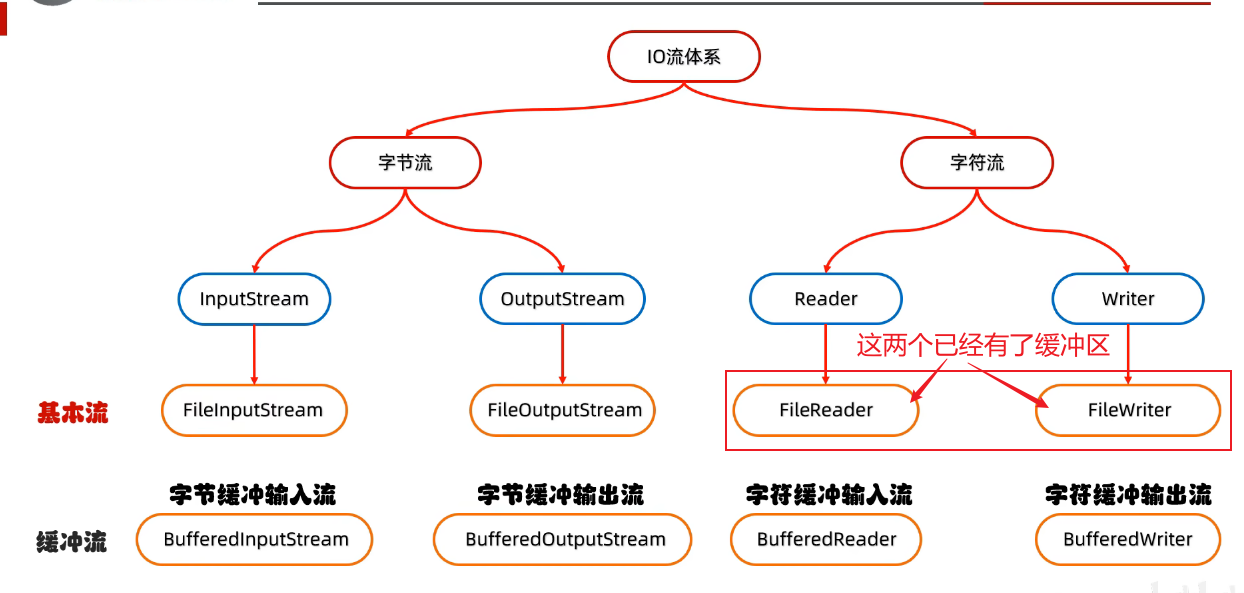
二、IO流的体系
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
三、字节流-操作本地文件
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、整体介绍
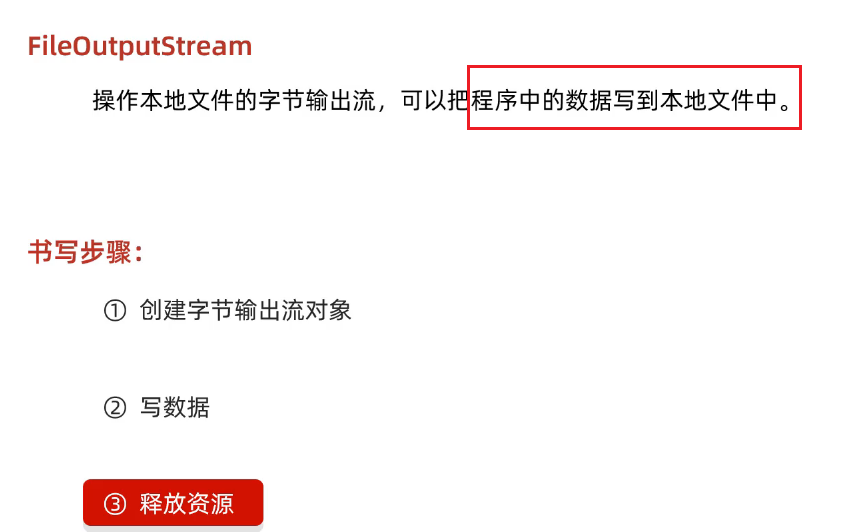
2、FileOutputStream
(1)书写步骤
(2)基本使用
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteOutputStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* //TODO 演示:字节输出流FileOutputStream
* 实现需求:写出一段文字到本地文件中。(暂时不写中文)
*
* 实现步骤:
* 创建对象
* 写出数据
* 释放资源
* */
//1.创建对象
//写出 输出流 OutputStream
//本地文件 FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\pyw\\a50bytestream\\temp\\a.txt");
//2.写出数据
fos.write(97);//输出a
//3。释放资源
fos.close();
}
}(3)书写细节

- ①创建字节输出流对象
- 细节1:参数是字符串表示的路径或者File对象都是可以的
- 细节2:如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件,但是要保证父级路径是存在的。
- 细节3:如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件
- ②写数据
- 细节:write方法的参数是整数,但是实际上写到本地文件中的是整数在ASCII上对应的字符
- ③释放资源
- 细节:每次使用完流之后都要释放资源,不然会被一直占用,其他人无法访问
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteOutputStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* //TODO 演示:字节输出流FileOutputStream
* 实现需求:写出一段文字到本地文件中。(暂时不写中文)
*
* 实现步骤:
* 创建对象
* 细节1:参数是字符串表示的路径或者是File对象都是可以的
* 细节2:文件不存在会创建新的文件,要保证父级路径是存在的
* 细节3:如果文件已存在则会清空文件
* 写出数据
* 细节:write方法的参数是整数,但实际上写道本地文件中的是整数在ASCII上对呀的字符
* 97 -> a
* 100-> d
* 释放资源
* 每次使用完流之后都要释放资源,不然会被一直占用,其他人无法访问
* */
//1.创建对象
//写出 输出流 OutputStream
//本地文件 FileOutputStream
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\pyw\\a50bytestream\\temp\\a.txt");
//2.写出数据
fos.write(97);//ASCII上对应的字符 -> 输出a
//3。释放资源
fos.close();
}
}(4)写出数据的三种方式
- void write(int b) 一次写一个字节数据
- void write(byte[] b) 一次写**一个字节数组**数据
- void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 一次写一个字节数组的部分数据
- 参数一:数组
- 参数二:起始索引 0
- 参数三:个数 3
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteOutputStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
//TODO
void write(int b) 一次写一个字节数据
void write(byte[] b) 一次写一个字节数组数据
void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) 一次写一个字节数组的部分数据
参数一:
数组
参数二:
起始索引 0
参数三:
个数 3
*/
//1.创建对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\pyw\\a50bytestream\\temp\\b.txt");
//2.写出数据
fos.write(97);//a
fos.write(98);//b
//传数组
byte[] arr = {97,98,99,100};
fos.write(arr); //a b c d
//从1索引开始写两个
fos.write(arr,1,2);//b c
//3.释放资源
fos.close();
}
}(5)换行和续写
换行写:
- 再次写出一个换行符就可以了
- windows:\r\n 回车换行
- Linux: \n
- Mac: \r
细节
- 在windows操作系统当中,java对回车换行进行了优化。
- 虽然完整的是\r\n,但是我们写其中一个\r或者\n,
- java也可以实现换行,因为java在底层会补全。
- 建议:不要省略,还是写全了。
续写(append):
- 如果想要续写,打开续写开关即可
- 开关位置:创建对象的第二个参数
- 默认false:表示关闭续写,此时创建对象会清空文件
- 手动传递true:表示打开续写,此时创建对象不会清空文件
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteOutputStreamDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
换行写:
再次写出一个换行符就可以了
windows: \r\n
Linux: \n
Mac: \r
细节:
在windows操作系统当中,java对回车换行进行了优化。
虽然完整的是\r\n,但是我们写其中一个\r或者\n,
java也可以实现换行,因为java在底层会补全。
建议:
不要省略,还是写全了。
续写:
如果想要续写,打开续写开关即可
开关位置:创建对象的第二个参数
默认false:表示关闭续写,此时创建对象会清空文件
手动传递true:表示打开续写,此时创建对象不会清空文件
*/
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\pyw\\a50bytestream\\temp\\c.txt",true);
String str1 = "helloworld";
byte[] bytes1 = str1.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes1);
//换行符
String wrap = "\r\n";
byte[] bytesWrap = wrap.getBytes();
fos.write(bytesWrap);
String str2 = "IO";
byte[] bytes2 = str2.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes2);
fos.close();
}
}(6)小结

3、FileInputStream
(1)书写步骤

(2)基本使用
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteInputStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* //TODO 演示:字节输入流FileInputStream
* 实现需求:读取文件中的数据。(暂时不写中文)
*
* 实现步骤:
* 创建对象
* 细节一:如果文件不存在,直接报错
* 读取数据
* 细节一:一次读取一个字节,读出来的是数据在ASCII码表上对应的数字
* 细节二:读到文件末尾了,read方法返回-1
* 释放资源
* 每次使用完流之后必须释放资源
* */
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\com\\pyw\\a50bytestream\\temp\\c.txt");
int read = fis.read();
System.out.println((char)read);
int read2 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char)read2);
int read3 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char)read3);
int read4 = fis.read();
System.out.println((char)read4);
fis.close();
}
}(3)细节

- 创建对象
- 细节一:如果文件不存在,直接报错
- 输出流:不存在,创建
- 把数据写到文件当中
- 输入流:不存在,而是报错呢?为什么不会像输出流一样创建呢?
- 因为创建出来的文件是没有数据的,没有任何意义。
- 所以Java就没有设计这种无意义的逻辑,文件不存在直接报错。
- 程序中最重要的是:数据。
- 读取数据
- 细节一:一次读取一个字节,读出来的是数据在ASCII码表上对应的数字
- 细节二:读到文件末尾了,read方法返回-1
- 若文件中的数据是**-1**,这时读取时,是分两部分读取,- 和 1 。
- 细节三:可以通过**强转读取到的数据类型**,获得数据。
- 释放资源
- 每次使用完流之后必须释放资源
(4)循环读取
注意:调用一个read就会读取一次,读取一次就会移动一次指针
- 所以**需要利用临时变量暂时保存**
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteInputStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
//TODO 字节输入流循环读取
*/
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\com\\pyw\\a50bytestream\\temp");
//注意:调用一个read就会读取一次,读取一次就会移动一次指针
// 需要利用临时变量暂时保存
int input;
while ((input = fis.read()) !=-1){
System.out.print((char)input);
}
fis.close();
}
}4、文件拷贝
规则:先开的最后再关闭
(1)拷贝较小文件
核心思想,边读边写
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
public class ByteInputStreamDemo4 {
/*
//拷贝文件
注:这个只能拷贝比较小的文件,大文件看后续文件夹
//练习,统计一下拷贝时间,单位毫秒
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\PYW\\Desktop\\day28-IO(字节流&字符流)\\笔记\\IO流(字节流&字符流).md");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\com\\pyw\\a50bytestream\\temp\\copy.md");
//2.拷贝
//核心思想,边读边写
Long start = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
int input;
while ((input = fis.read()) != -1){
fos.write(input);
}
Long end = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(end - start + " ms");
//规则:先开的最后再关闭
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}(2)文件拷贝的问题

①原因-一次读取一个字节
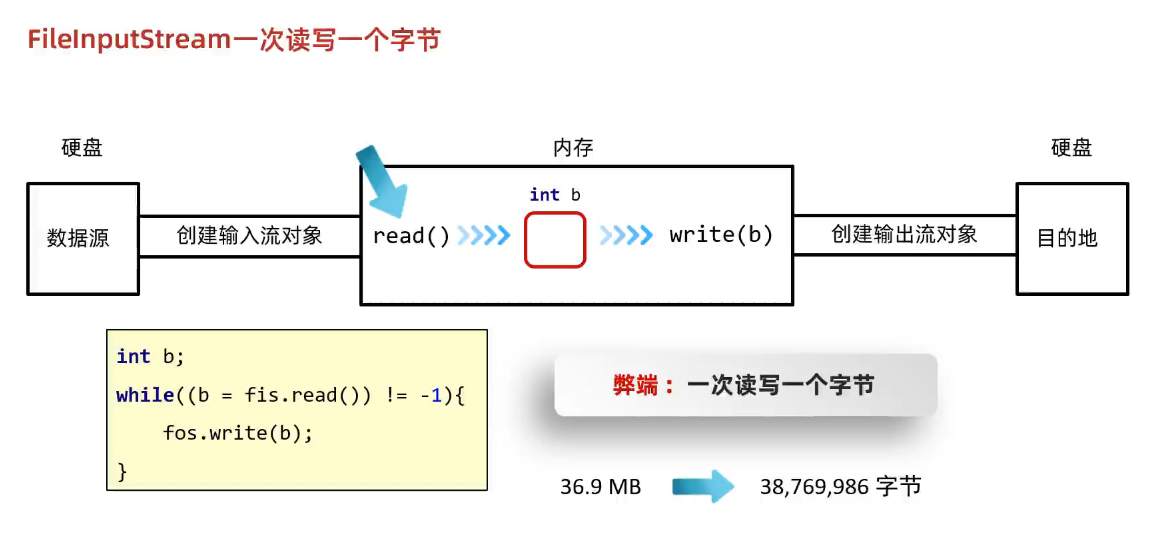
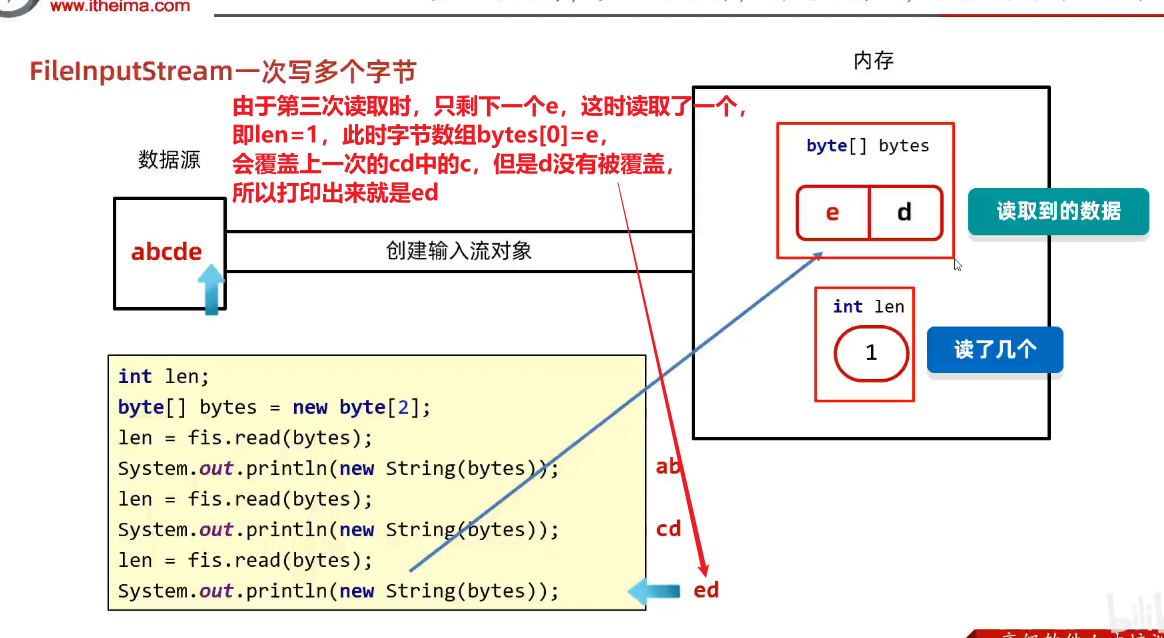
②解决办法-一次读取多个字节-字节数组
1)基本实现
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteInputStreamDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
public int read(byte[] buffer) 一次读一个字节数组数据
文件内容 abcde
*/
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");
//2.读取数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[2];
//一次读取多个字节数据,具体读多少,跟数组的长度有关
//返回值:本次读取到了多少个字节数据
int len1 = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len1);//读取了2个
String str1 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(str1); //ab 不是97 98是因为new String()形参是byte数组的话,会自动转成字符拼接成字符串
int len2 = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len2);//2
String str2 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(str2); //cd
int len3 = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len3);// 1
String str3 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(str3);// ed //e只覆盖了cd中的c,d还未被覆盖
//3.释放资源
fis.close();
}
}2)读多少写多少-避免覆盖问题
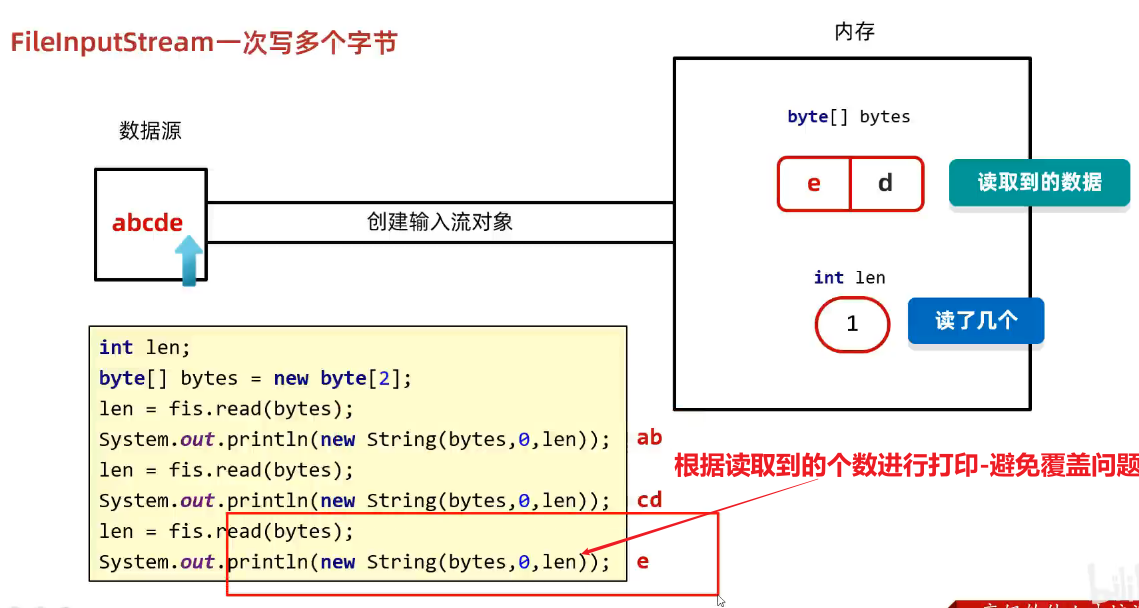
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteInputStreamDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
public int read(byte[] buffer) 一次读一个字节数组数据
文件内容 abcde
*/
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");
//2.读取数据
byte[] bytes = new byte[2];
//一次读取多个字节数据,具体读多少,跟数组的长度有关
//返回值:本次读取到了多少个字节数据
int len1 = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len1);//读取了2个
String str1 = new String(bytes,0,len1);
System.out.println(str1);
int len2 = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len2);//2
String str2 = new String(bytes,0,len2);
System.out.println(str2);
int len3 = fis.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len3);// 1
String str3 = new String(bytes,0,len3);
System.out.println(str3);// e
//3.释放资源
fis.close();
}
}(3)文件拷贝的改进
字节数组的大小为1024的整数倍
package com.itheima.mybytestream2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteStreamDemo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 练习:
* 文件拷贝
* 把D:\itheima\movie.mp4 (16.8 MB) 拷贝到当前模块下。
*
* */
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\itheima\\movie.mp4");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.mp4");
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];//一次读取5兆的数据
//一次读取多个字节数据,具体读多少时跟数组长度有关的
//返回值:本次读取到了多少个字节数据
//并且会把本次读取的数据放到数组当中
while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//3.释放资源
fos.close();
fis.close();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
}四、IO流中不同JDK版本捕获异常的方式
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟

1、普通捕获异常并释放资源
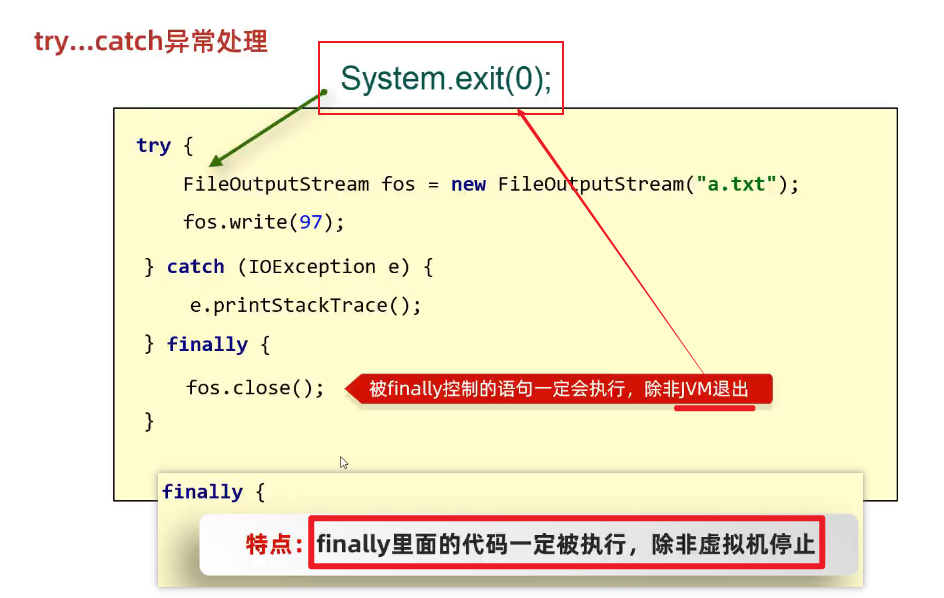
package com.pyw.a50bytestream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteStreamErrDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
*
* 利用try...catch...finally捕获拷贝文件中代码出现的异常
*
*
* */
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\itheima\\movie.mp4");
fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.mp4");
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];
while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//3.释放资源
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}2、JDK7-IO流中捕获异常的写法
package com.itheima.mybytestream2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteStreamDemo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
*
* JDK7:IO流中捕获异常的写法
*
* try后面的小括号中写创建对象的代码,
* 注意:只有实现了AutoCloseable接口的类,才能在小括号中创建对象。
* try(){
*
* }catch(){
*
* }
*
* */
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\itheima\\movie.mp4");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.mp4")) {
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3、JDK9-IO流中捕获异常的写法
package com.itheima.mybytestream2;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteStreamDemo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
/*
*
* JDK9:IO流中捕获异常的写法
*
*
* */
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\itheima\\movie.mp4");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.mp4");
try (fis;fos) {
//2.拷贝
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024 * 1024 * 5];
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}五、字符集
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟


1、ASCLL
(1)ASCLL表
(2)ASCLL的编解码过程

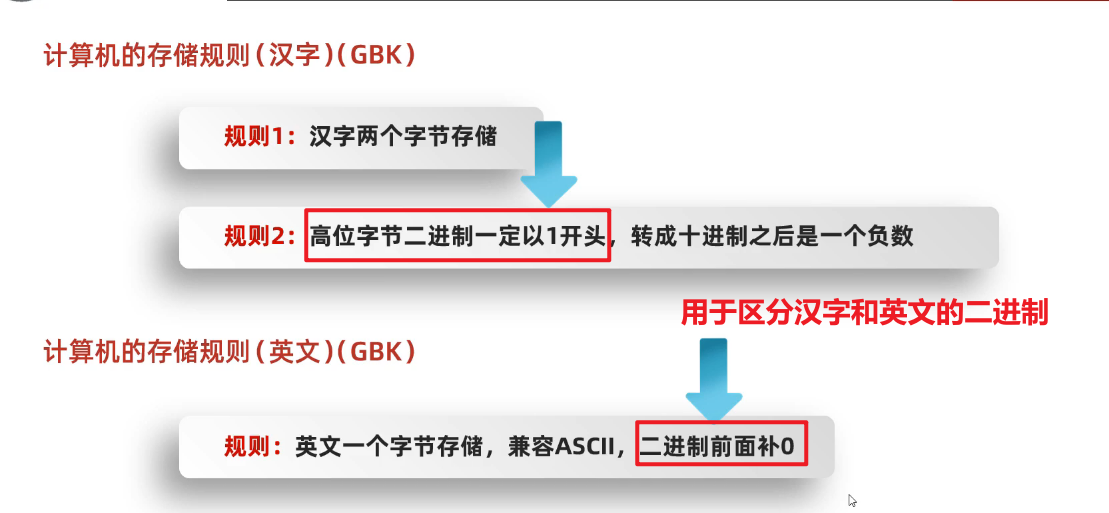
2、GBK
(1)GBK-Windows系统显示ANSI

(2)GBK的编解码过程
①英文

②中文


1)练习
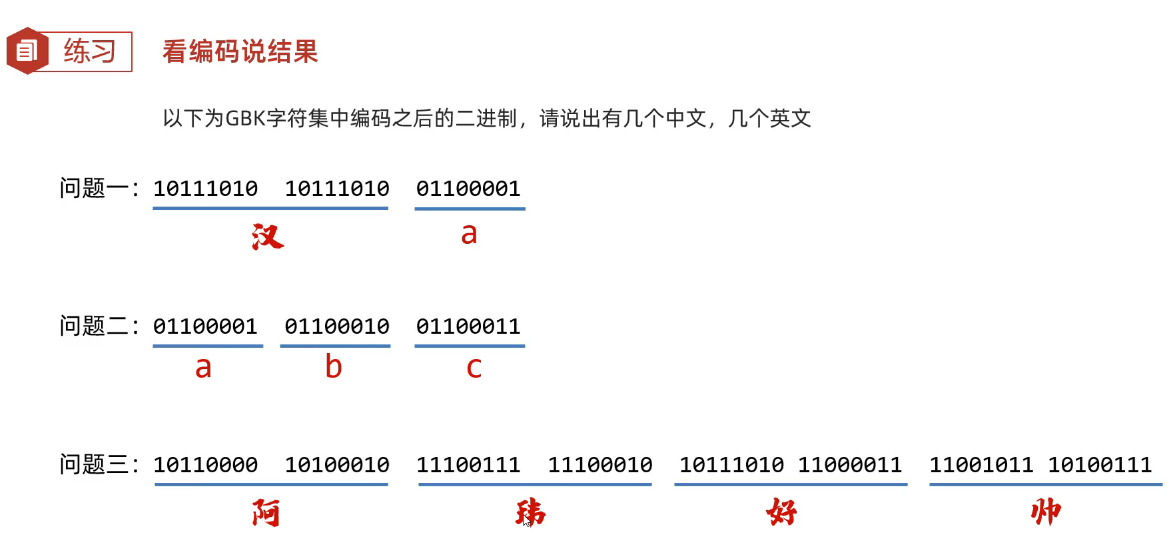
3、ASCLL和GBK小结

4、Unicode

(1)UTF的编码方式
①英文-UTF-16和UTF-32

②UTF-8编码方式
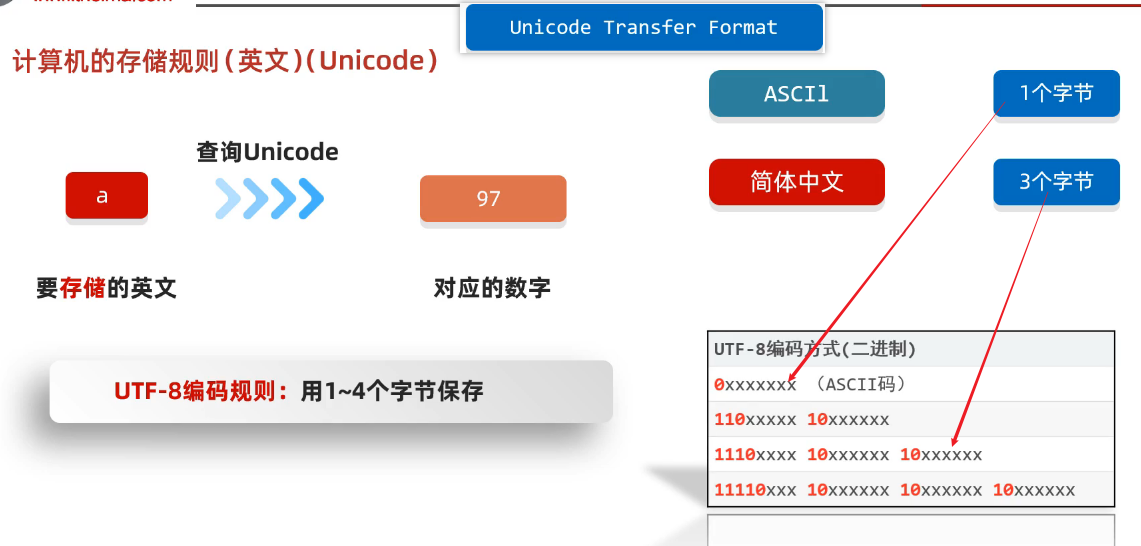
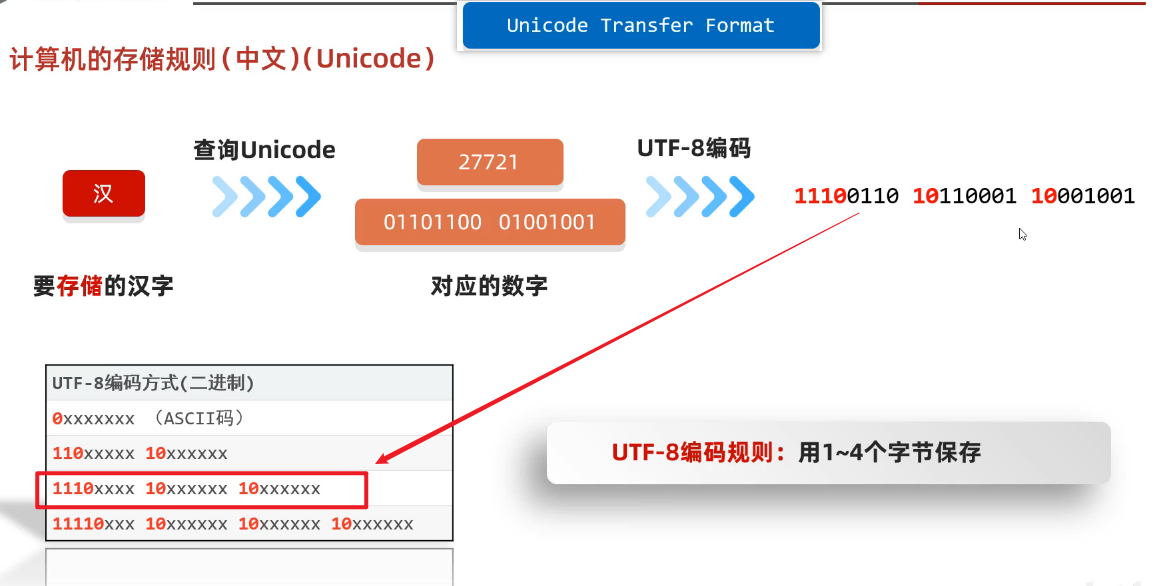
1)练习题1-UTF-8是一种编码方式

2)练习题2

(2)小结

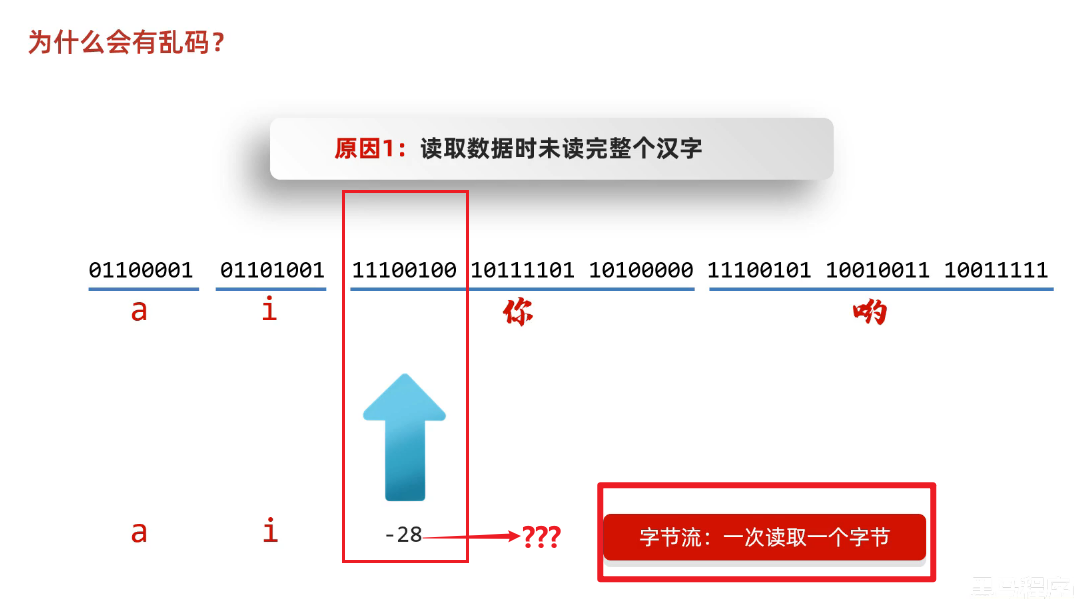
六、为什么会有乱码?
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟

1、读取数字是未读完整个汉字
2、编码和解码时的方式不一致

(1)编解码方式一致
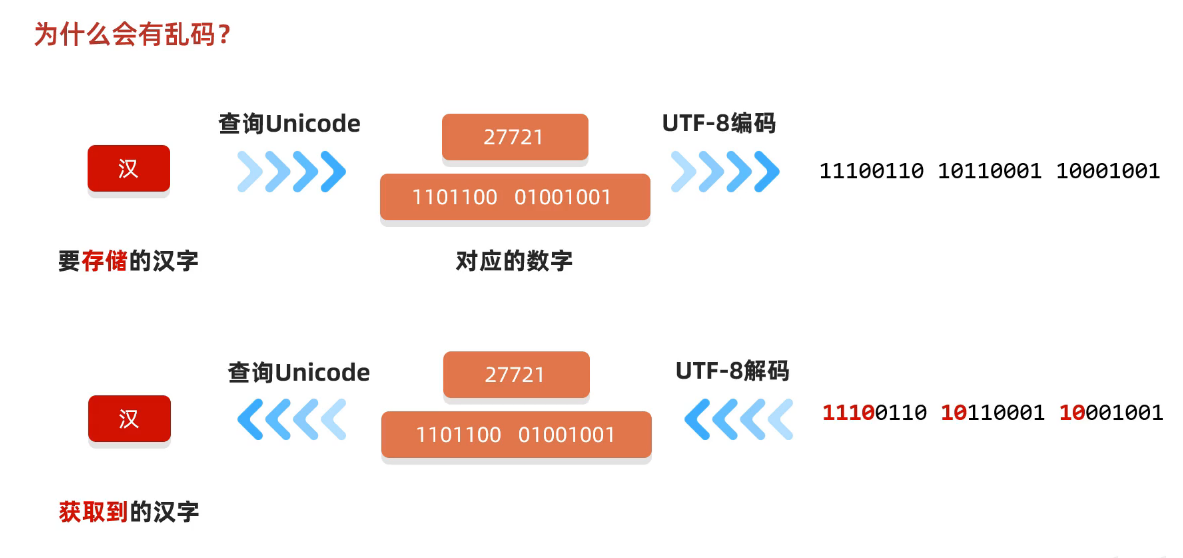
(2)编解码方式不一致
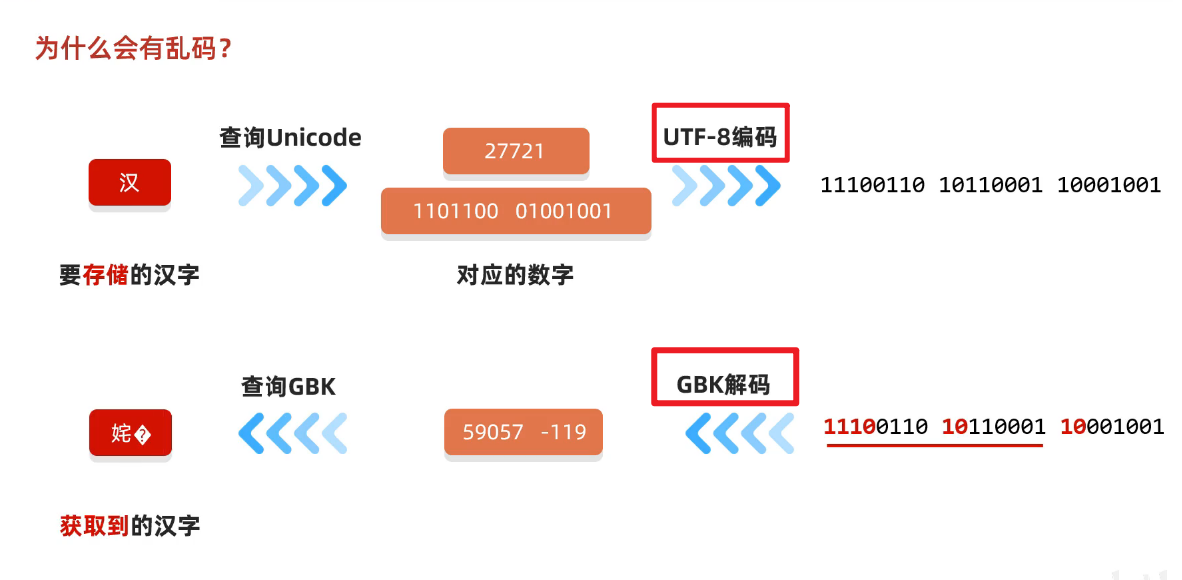
3、如何不产生乱码

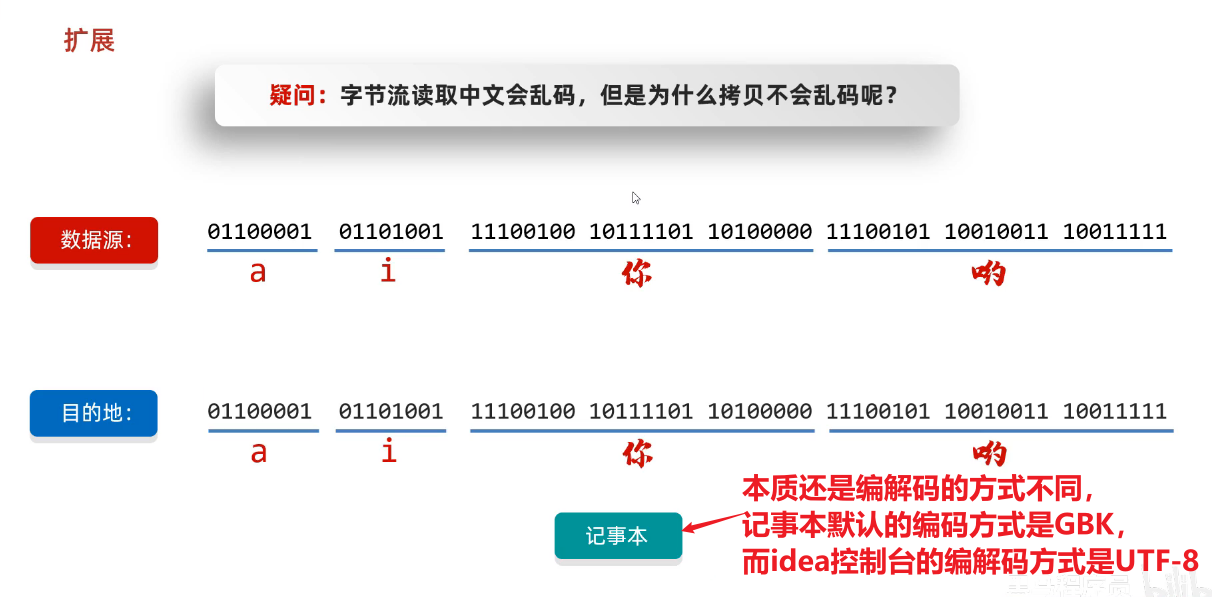
4、扩展

字节流读取中文-出现乱码
package com.itheima.mycharset;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharSetDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
字节流读取中文会出现乱码
*/
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)b);
}
fis.close();
}
}
文件拷贝后,新文件的中文不会乱码
package com.itheima.mycharset;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharSetDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt");
//2.拷贝
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1){
fos.write(b);
}
//3.释放资源
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
七、Java中的编解码方法
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
package com.itheima.mycharset;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CharSetDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
/*
Java中编码的方法
public byte[] getBytes() 使用默认方式进行编码
public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) 使用指定方式进行编码
Java中解码的方法
String(byte[] bytes) 使用默认方式进行解码
String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName) 使用指定方式进行解码
*/
//1.编码
String str = "ai你哟";
byte[] bytes1 = str.getBytes(); //idea默认使用utf-8
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1)); //8个字节
byte[] bytes2 = str.getBytes("GBK"); //指定编码方式
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2)); //6个字节
//2.解码
String str2 = new String(bytes1); //默认解码方式utf-8
System.out.println(str2);
String str3 = new String(bytes1,"GBK");
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
八、字符流-操作本地文件
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、字符流的概念和特点
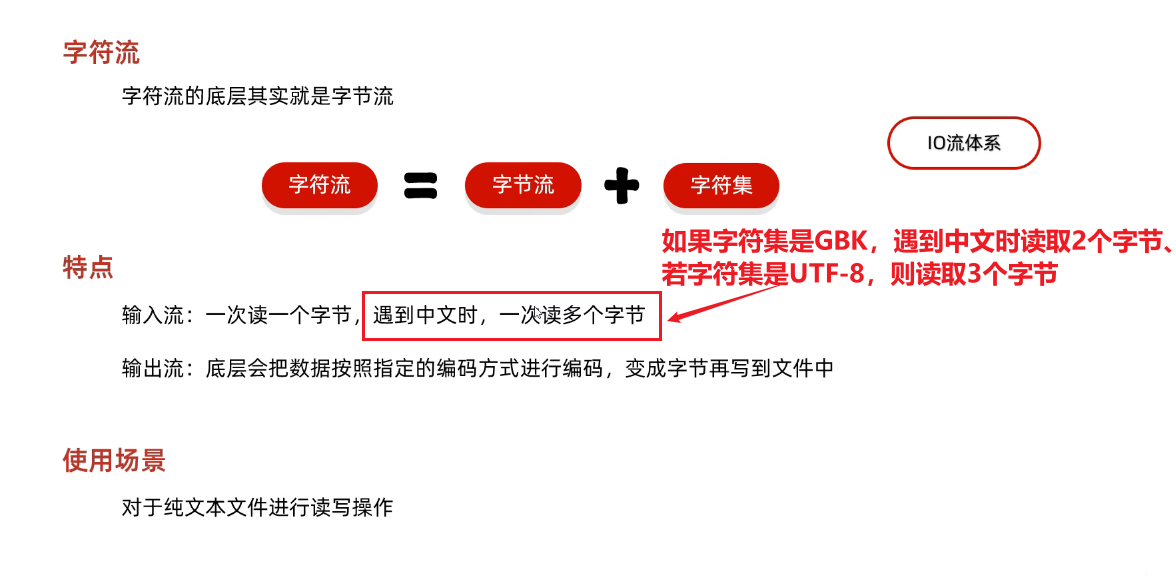
2、使用场景

3、字符流的继承体系
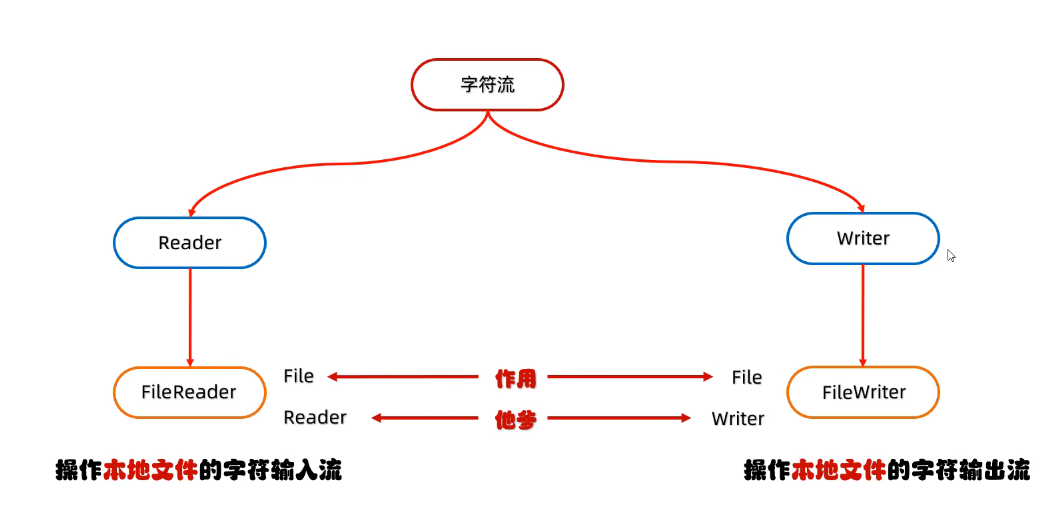
4、FileReader-字符输入流
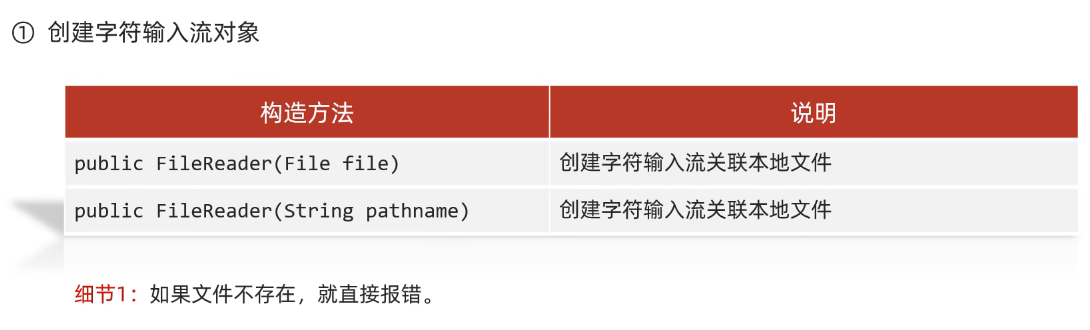
(1)创建字符流输入对象
(2)读取数据-按字节进行读取

①细节
读取数据 read()
- 字符流的底层也是字节流,默认也是一个字节一个字节的读取的。
- 如果**遇到中文就会一次读取多个**,GBK一次读两个字节,UTF-8一次读三个字节
read()细节:
1.read():默认也是一个字节一个字节的读取的,如果遇到中文就会一次读取多个
2.在读取之后,方法的底层还会进行解码并转成十进制。最终把这个十进制作为返回值这个十进制的数据也表示在字符集上的数字
- 英文:文件里面二进制数据 0110 0001
- read方法进行读取,解码并转成十进制97
- 中文:文件里面的二进制数据 11100110 10110001 10001001
- read方法进行读取,解码并转成十进制27721
- 我想看到中文汉字,就是把这些十进制数据,再进行强转就可以了
- 英文:文件里面二进制数据 0110 0001
②示例代码
package com.itheima.mycharstream1;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
第一步:创建对象
public FileReader(File file) 创建字符输入流关联本地文件
public FileReader(String pathname) 创建字符输入流关联本地文件
第二步:读取数据
public int read() 读取数据,读到末尾返回-1
public int read(char[] buffer) 读取多个数据,读到末尾返回-1
第三步:释放资源
public void close() 释放资源/关流
*/
//1.创建对象并关联本地文件
FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\a.txt");
//2.读取数据 read()
//字符流的底层也是字节流,默认也是一个字节一个字节的读取的。
//如果遇到中文就会一次读取多个,GBK一次读两个字节,UTF-8一次读三个字节
//read()细节:
//1.read():默认也是一个字节一个字节的读取的,如果遇到中文就会一次读取多个
//2.在读取之后,方法的底层还会进行解码并转成十进制。
// 最终把这个十进制作为返回值
// 这个十进制的数据也表示在字符集上的数字
// 英文:文件里面二进制数据 0110 0001
// read方法进行读取,解码并转成十进制97
// 中文:文件里面的二进制数据 11100110 10110001 10001001
// read方法进行读取,解码并转成十进制27721
// 我想看到中文汉字,就是把这些十进制数据,再进行强转就可以了
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
//3.释放资源
fr.close();
}
}(3)读取数据-按字符数组进行读取
①细节
- read(chars):读取数据,解码,强转三步合并了,把强转之后的字符放到数组当中
- 空参的read + 强转类型转换
- 字符数组的长度,用来==设置每次读取字符的长度==
- read(char[])返回的是这次读取的字符个数
- System.out.print(new String(chars,0,len));
- 利用0,len进行获取当前读取的字符-避免出现覆盖的问题
②示例代码
package com.itheima.mycharstream1;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
第一步:创建对象
public FileReader(File file) 创建字符输入流关联本地文件
public FileReader(String pathname) 创建字符输入流关联本地文件
第二步:读取数据
public int read() 读取数据,读到末尾返回-1
public int read(char[] buffer) 读取多个数据,读到末尾返回-1
第三步:释放资源
public void close() 释放资源/关流
*/
//1.创建对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\a.txt");
//2.读取数据
char[] chars = new char[2]; //字符数组的长度,用来设置每次读取字符的长度
int len;
//read(chars):读取数据,解码,强转三步合并了,把强转之后的字符放到数组当中
//空参的read + 强转类型转换
while((len = fr.read(chars)) != -1){ //read(char[])返回的是这次读取的字符个数
//把数组中的数据变成字符串再进行打印
System.out.print(new String(chars,0,len));//利用0,len进行获取当前读取的字符-避免出现覆盖的问题
}
//3.释放资源
fr.close();
}
}(4)释放资源

5、FileWriter-字符输出流
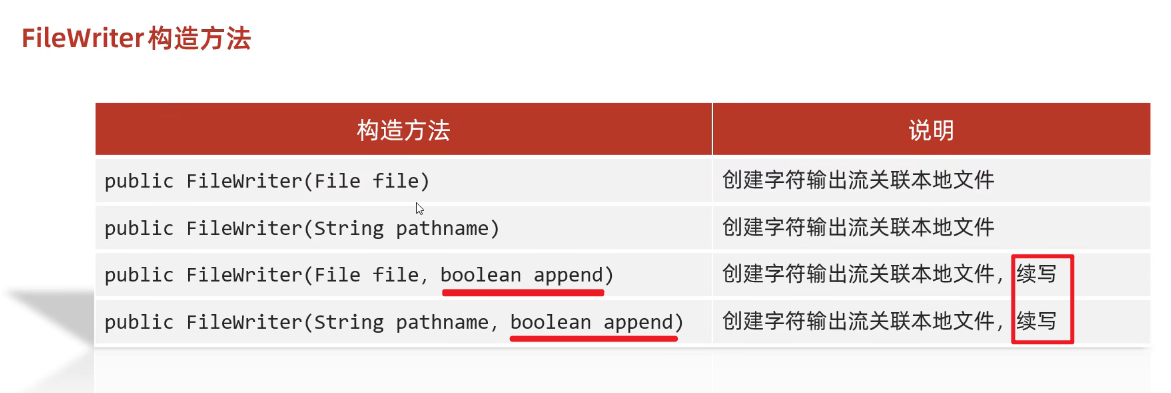
(1)构造方法
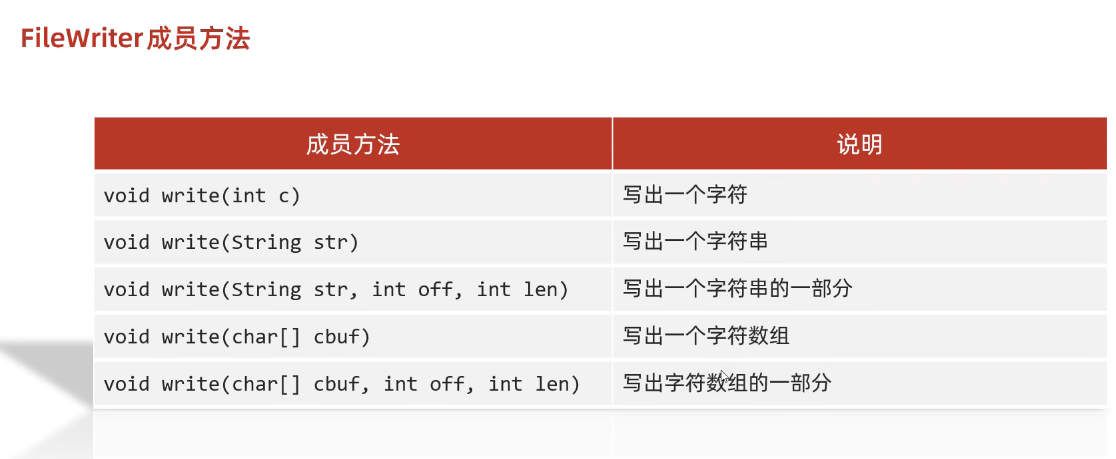
(2)写出字符的方法
(3)书写细节

- 创建字符输出流对象
- 细节1:参数是字符串表示的路径或者File对象都是可以的
- 细节2:如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件,但是要保证父级路径是存在的
- 细节3:如果文件已经存在,则会清空文件,如果不想清空可以打开续写开关
- 写数据
- 细节:如果write方法的参数是整数,但是实际上写到本地文件中的是整数在字符集上对应的字符
- 释放资源
- 细节:每次使用完流之后都要释放资源
(4)示例代码
package com.itheima.mycharstream1;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
第一步:创建对象
public FileWriter(File file) 创建字符输出流关联本地文件
public FileWriter(String pathname) 创建字符输出流关联本地文件
public FileWriter(File file, boolean append) 创建字符输出流关联本地文件,续写
public FileWriter(String pathname, boolean append) 创建字符输出流关联本地文件,续写
第二步:读取数据
void write(int c) 写出一个字符
void write(String str) 写出一个字符串
void write(String str, int off, int len) 写出一个字符串的一部分
void write(char[] cbuf) 写出一个字符数组
void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) 写出字符数组的一部分
第三步:释放资源
public void close() 释放资源/关流
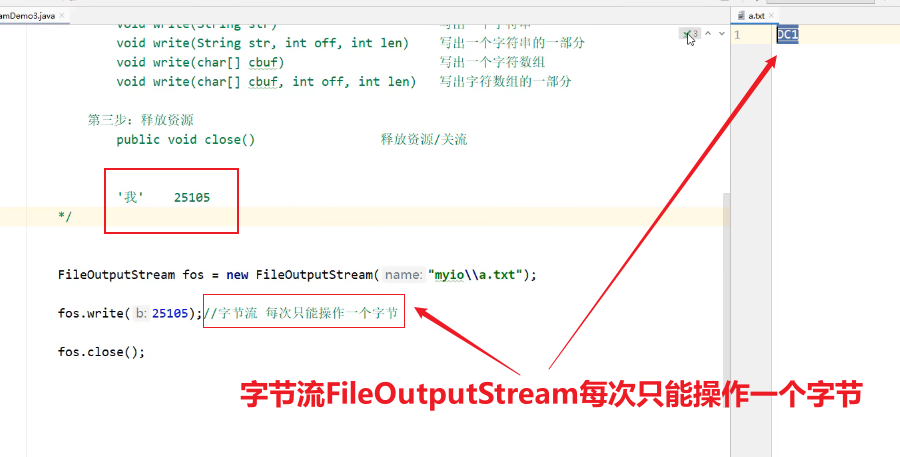
'我' 25105
*/
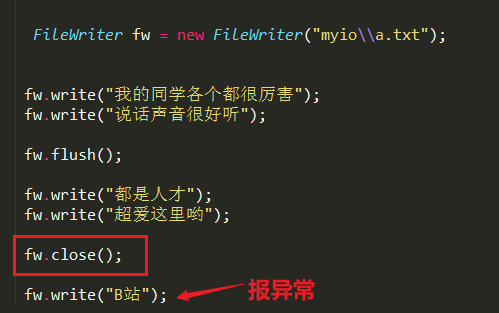
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\a.txt",true);
//fw.write(25105); //根据字符集的编码方式进行编码,把编码之后的数据写到文件中去
//fw.write("你好威啊???");
char[] chars = {'a','b','c','我'};
fw.write(chars);
fw.close();
}
}(5)字节流和字符流的区别
6、字符输入流-原理解析-缓冲区
(1)原理解析
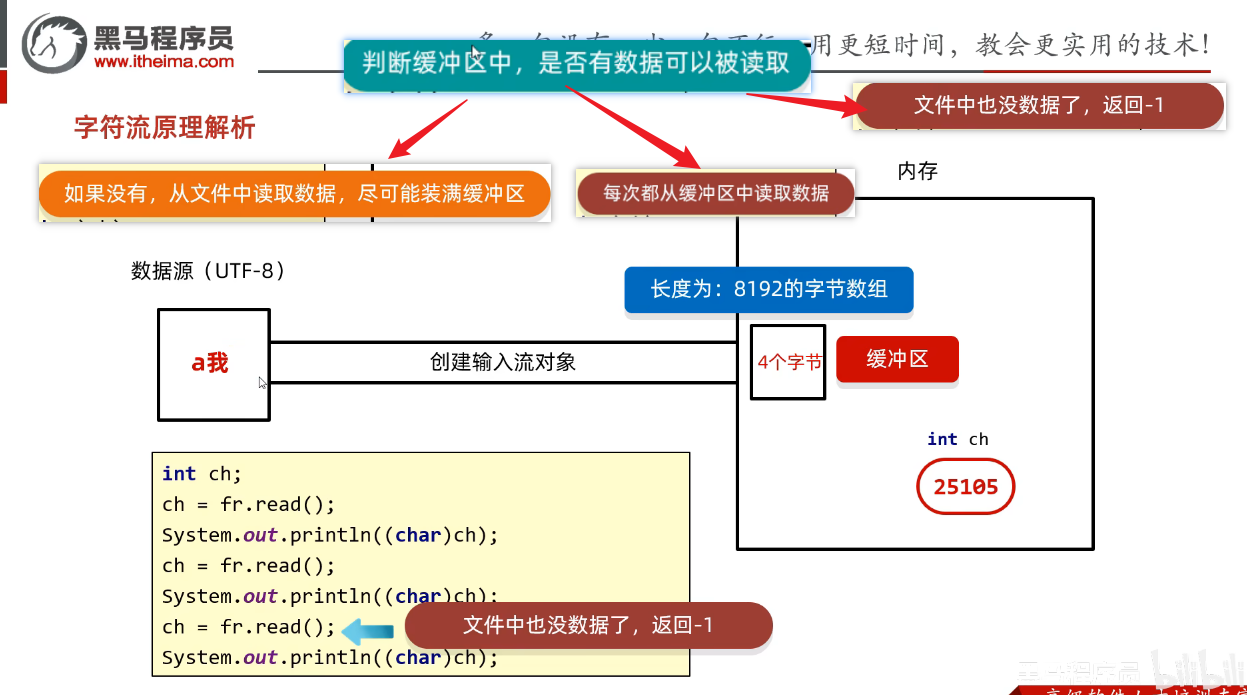

- 创建字符输入流对象
- 底层:关联文件,并创建缓冲区(长度为8192的字节数组)
- 如果读取的缓冲区的长度超过了8192,则会从0索引位置开始覆盖原有的数据
- 底层:关联文件,并创建缓冲区(长度为8192的字节数组)
- 读取数据
- 底层:
- 1.判断缓冲区中是否有数据可以读取
- 2.缓冲区没有数据:就从文件中获取数据,装到缓冲区中,每次尽可能装满缓冲区如果文件中也没有数据了,返回-1
- 3.缓冲区有数据:就从缓冲区中读取。
- 空参的read方法:一次读取一个字节,遇到中文一次读多个字节,把字节解码并转成十进制返回
- 有参的read方法:把读取字节,解码,强转三步合并了,强转之后的字符放到数组中
- 底层:
(2)细节
①读取长度超过字节缓冲区8192
- 底层:关联文件,并创建缓冲区(长度为8192的字节数组)
- 如果读取的缓冲区的长度超过了8192,则会从0索引位置开始覆盖原有的数据
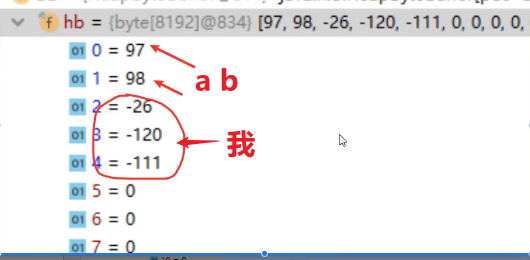
②读取一次后使用FileWriter清空了文件
- reade()读取一次后,会把文件中的数据放到缓冲区当中
- 只能**读取缓冲区中的数据**,文件中剩余的数据无法再次读取
package com.itheima.mycharstream1;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharStreamDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\b.txt");
fr.read();//会把文件中的数据放到缓冲区当中
//没有设置append属性为true,创建字符输出流式默认会清空文件
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\b.txt");
//请问,如果我再次使用fr进行读取
//会读取到数据吗?
//会把缓冲区中的数据全部读取完毕
//正确答案:
//但是只能读取缓冲区中的数据,文件中剩余的数据无法再次读取
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.println((char)ch);
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
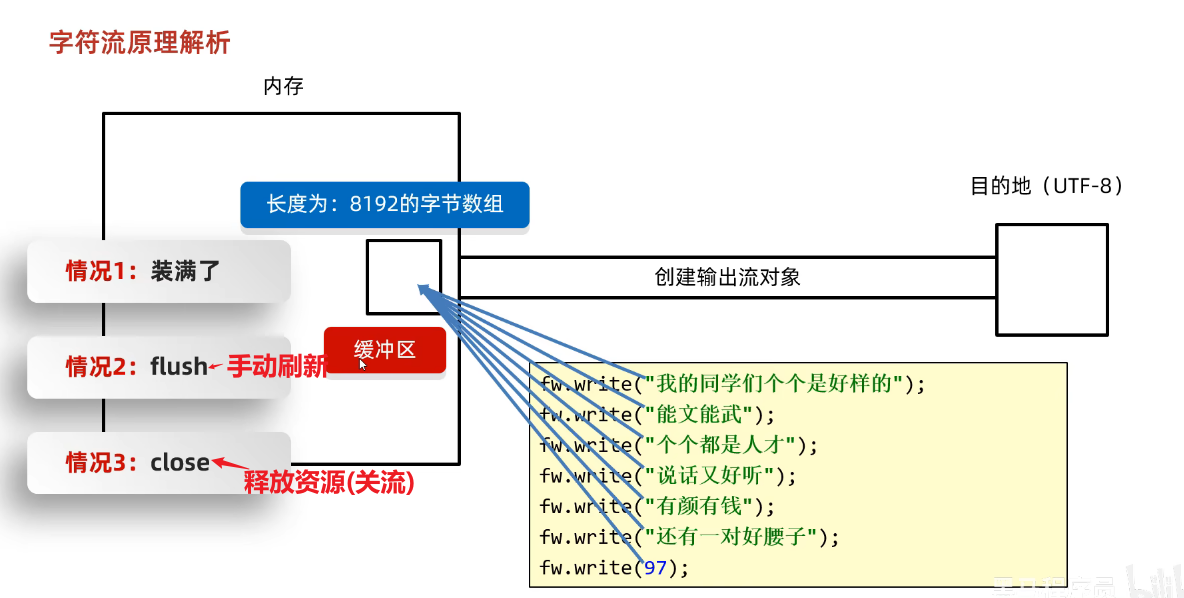
}7、字符输出流-原理解析-缓冲区
(1)原理解析
(2)flush和close方法
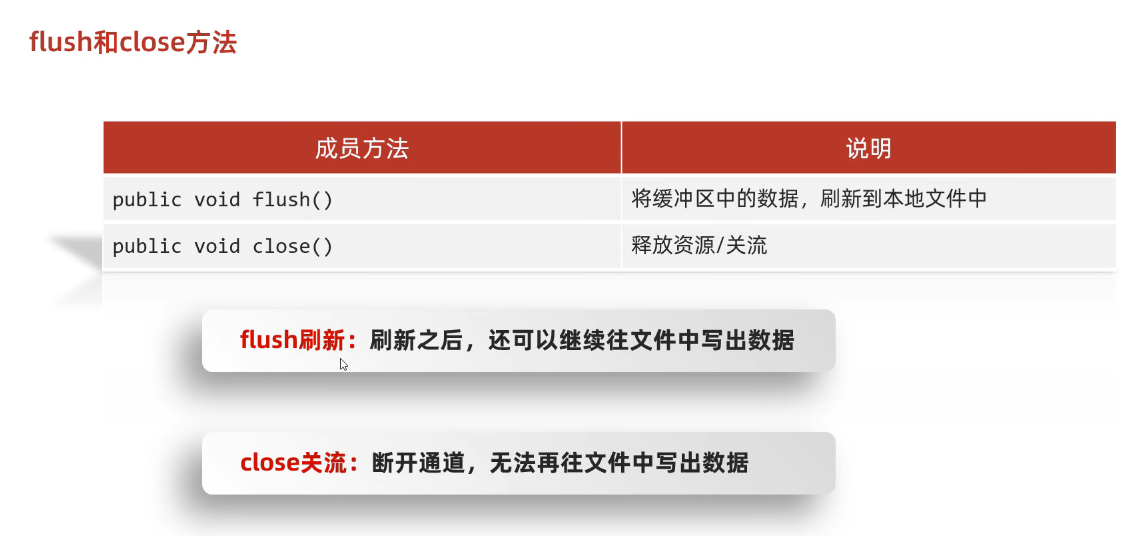
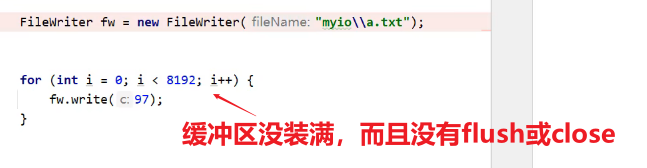
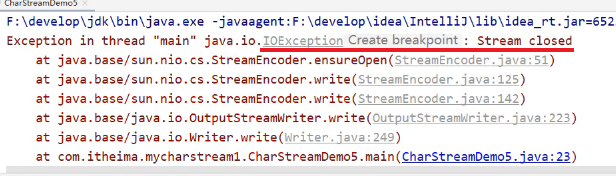
(3)细节
- 如果既没有使用flush手动刷新,也没有使用close关流,而且程序这个过程也**没有把缓冲区装满,则文件不会被写入任何数据**。
- 如果已经使用close关闭流后,不能在写入数据了
九、字节流和字符流的使用场景
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟


十、综合练习1
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、拷贝文件夹

package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//拷贝一个文件夹,考虑子文件夹
//1.创建对象表示数据源
File src = new File("D:\\aaa\\src");
//2.创建对象表示目的地
File dest = new File("D:\\aaa\\dest");
//3.调用方法开始拷贝
copydir(src,dest);
}
/*
* 作用:拷贝文件夹
* 参数一:数据源
* 参数二:目的地
*
* */
private static void copydir(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
dest.mkdirs(); //创建文件夹,不存在则会创建,存在的话会失败,但不会报错
//递归
//1.进入数据源
File[] files = src.listFiles();
if (files == null) { //判断=空文件夹,有些文件没有权限访问,会返回null
System.out.println("空文件夹或权限不够:" + src.getAbsolutePath());
return;
}
//2.遍历数组
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
//3.判断文件,拷贝
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,file.getName()));
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}else {
//4.判断文件夹,递归
copydir(file, new File(dest,file.getName())); //父级和子级
}
}
}
}
2、文件加密和解密

package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.*;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
为了保证文件的安全性,就需要对原始文件进行加密存储,再使用的时候再对其进行解密处理。
加密原理:
对原始文件中的每一个字节数据进行更改,然后将更改以后的数据存储到新的文件中。
解密原理:
读取加密之后的文件,按照加密的规则反向操作,变成原始文件。
^ : 异或
两边相同:false
两边不同:true
0:false
1:true
100:1100100
10: 1010
100^10 = 110
110^10 = 100 对异或的结果110再次异或会回到100
//特点: 一个数 连续异或两次相同的数 会回到原来的
1100100
^ 0001010
__________
1101110
^ 0001010
__________
1100100
得出结论:一个数字异或同一个数字两次会得到本身
*/
//加密
encryptionAndReduction(
new File("src/com/pyw/a53streamtest/temp/girl.png"),
new File("src/com/pyw/a53streamtest/temp/secret.png")
);
//解密
encryptionAndReduction(
new File("src/com/pyw/a53streamtest/temp/secret.png"),
new File("src/com/pyw/a53streamtest/temp/result.png")
);
}
public static void encryptionAndReduction(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
//1.创建对象关联原始文件
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b ^ 2);
}
//4.释放资源
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}3、修改文件中的数据-排序
package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
文本文件中有以下的数据:
2-1-9-4-7-8
将文件中的数据进行排序,变成以下的数据:
1-2-4-7-8-9
*/
//1.读取数据
FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\a.txt");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read()) != -1){
sb.append((char)ch);
}
fr.close();
System.out.println(sb);
//2.排序
String str = sb.toString();
String[] arrStr = str.split("-");//2-1-9-4-7-8
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String s : arrStr) {
int i = Integer.parseInt(s);
list.add(i);
}
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
//3.写出
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\a.txt");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(i == list.size() - 1){
fw.write(list.get(i) + "");
}else{
fw.write(list.get(i) + "-");
}
}
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\a.txt");
StringJoiner sj = new StringJoiner("-","",""); //StringJoiner指定规则拼接字符串
for (Integer integer : list) {
sj.add(integer+"");
}
fw.write(sj.toString());
fw.close();
}
}
改进版
- 细节1:
- 带读取的文件中的数据不要换行,回隐含\r\n
- 细节2:
- bom头占三个字节:文件的信息
package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
文本文件中有以下的数据:
2-1-9-4-7-8
将文件中的数据进行排序,变成以下的数据:
1-2-4-7-8-9
细节1:
带读取的文件中的数据不要换行,回隐含\r\n
细节2:
bom头占三个字节:文件的信息
*/
//1.读取数据
FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\a.txt");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int ch;
while((ch = fr.read()) != -1){
sb.append((char)ch);
}
fr.close();
System.out.println(sb);
//2.排序
Integer[] arr = Arrays.stream(sb.toString()
.split("-"))
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.sorted()
.toArray(Integer[]::new);
//3.写出
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\a.txt");
String s = Arrays.toString(arr).replace(", ","-");
String result = s.substring(1, s.length() - 1);
fw.write(result);
fw.close();
}
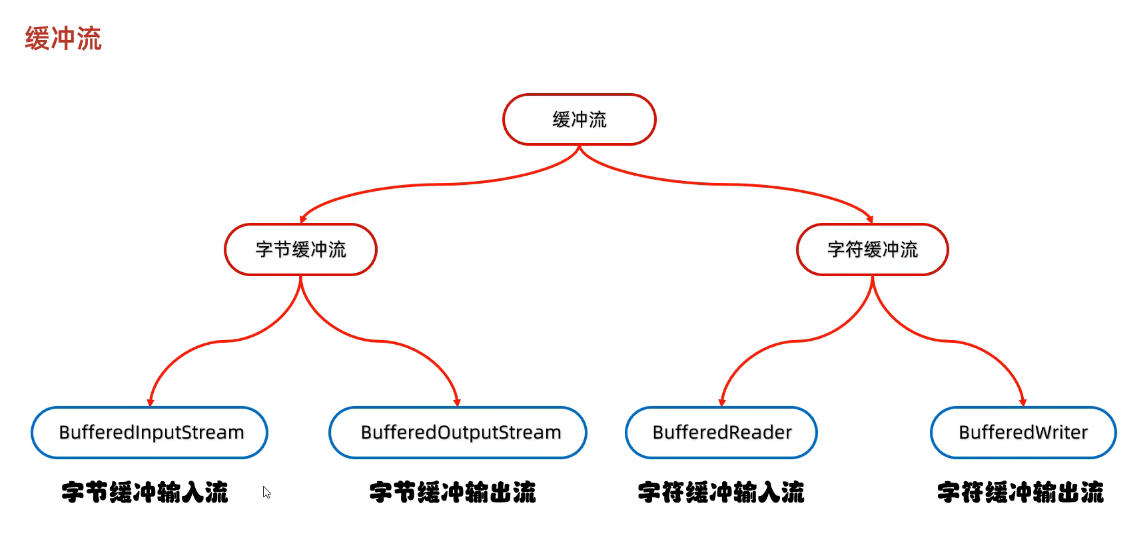
}十一、缓冲流
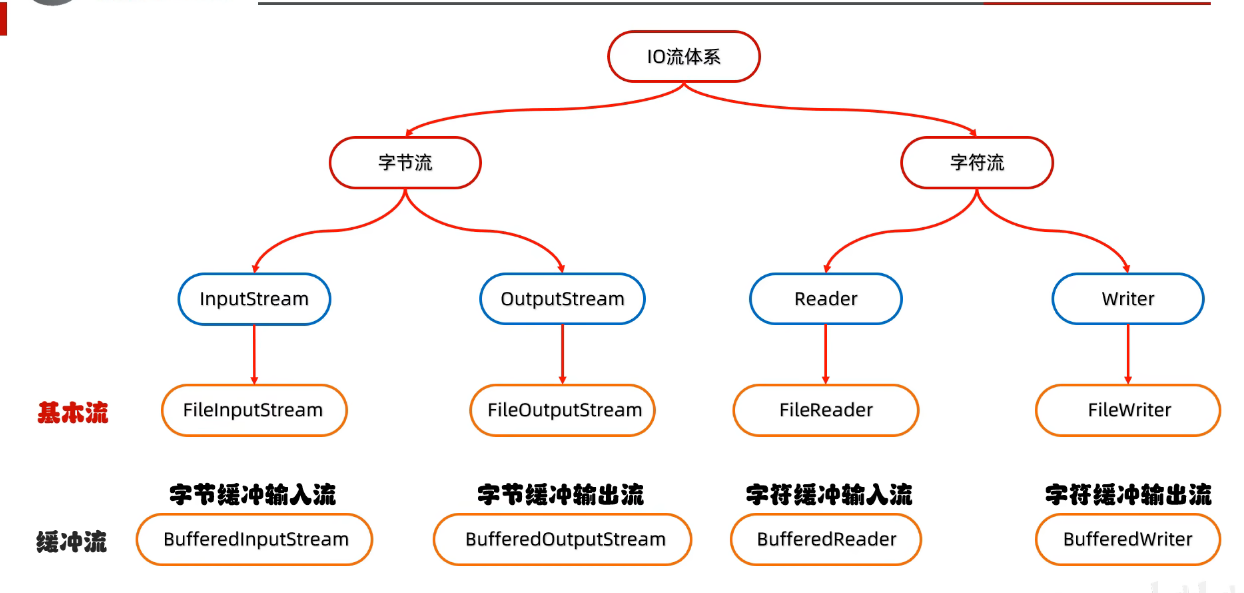
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、字节缓冲流-BufferedInput/(Output)Stream
(1)体系
(2)构造方法

(3)基本使用-拷贝文件
①示例代码-BufferedInput(Out)Stream
package com.itheima.mybufferedstream1;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 需求:
* 利用字节缓冲流拷贝文件
*
* 字节缓冲输入流的构造方法:
* public BufferedInputStream(InputStream is)
*
* 字节缓冲输出流的构造方法:
* public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream os)
*
* */
//1.创建缓冲流的对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt"));
//2.循环读取并写到目的地
int b;
while ((b = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(b);
}
//3.释放资源
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}一次读写多个字节-byte字节数组
package com.itheima.mybufferedstream1;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 需求:
* 利用字节缓冲流拷贝文件
*
* 字节缓冲输入流的构造方法:
* public BufferedInputStream(InputStream is)
*
* 字节缓冲输出流的构造方法:
* public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream os)
*
* */
//1.创建缓冲流的对象
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy2.txt"));
//2.拷贝(一次读写多个字节)
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//3.释放资源
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
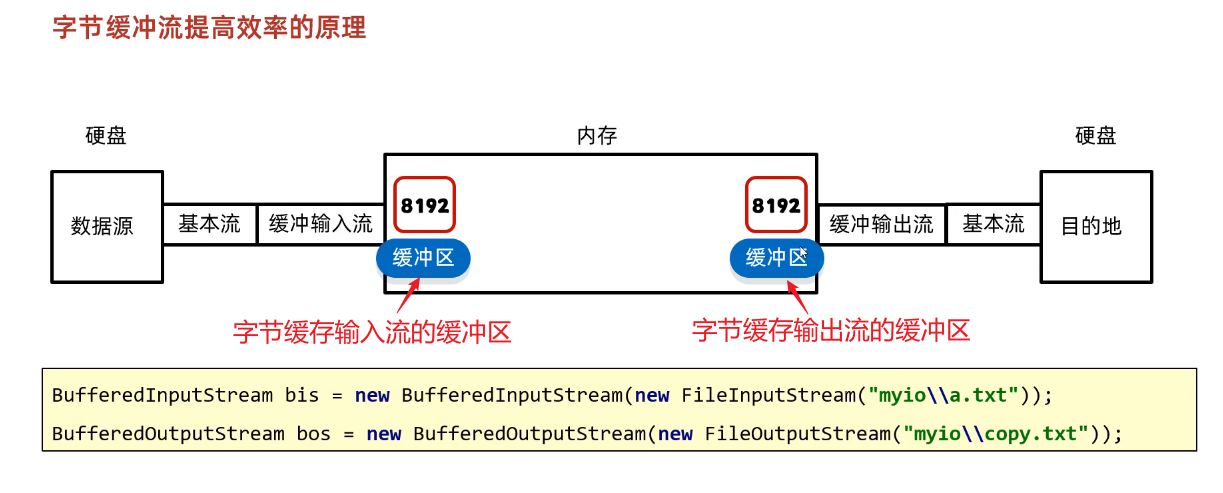
}(4)读写原理
①创建缓冲区
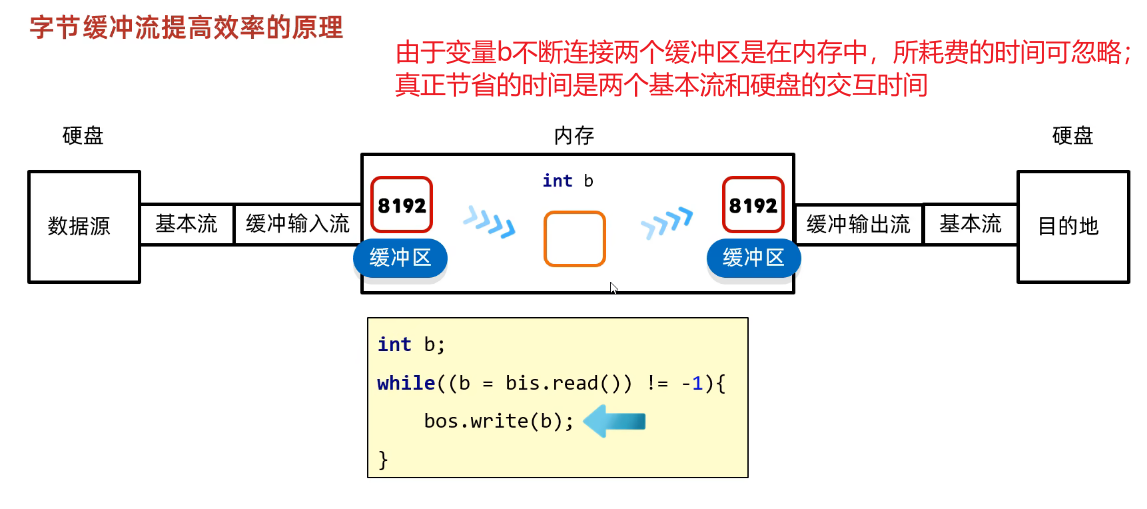
②变量传递--连接两个缓冲区
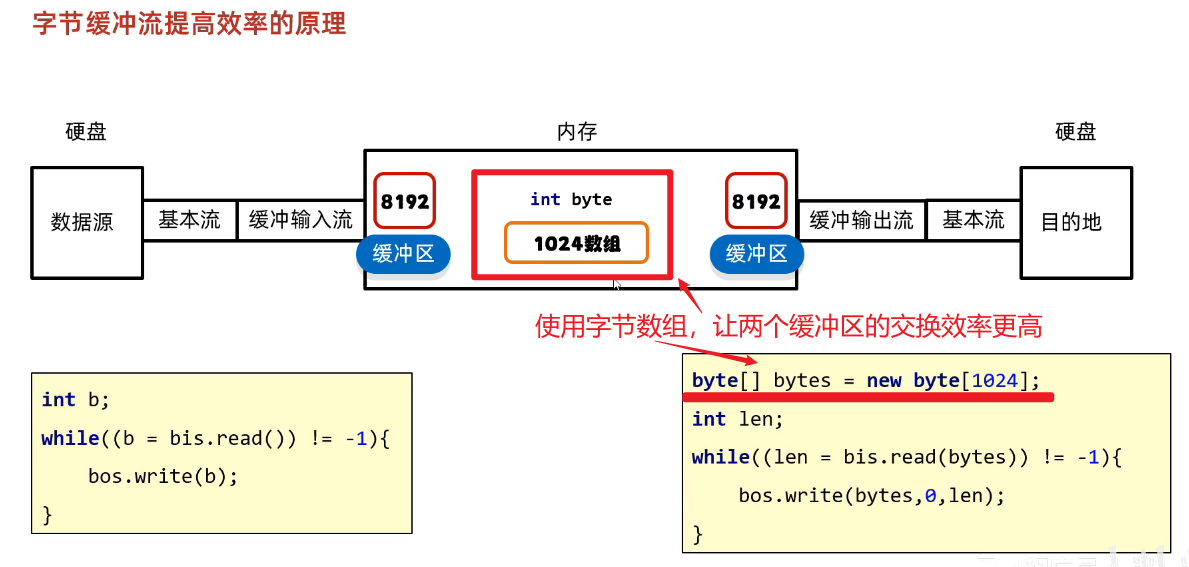
③字节数组传递--连接两个缓冲区
2、字符缓冲流-BufferedReader/(Writer)
(1)体系
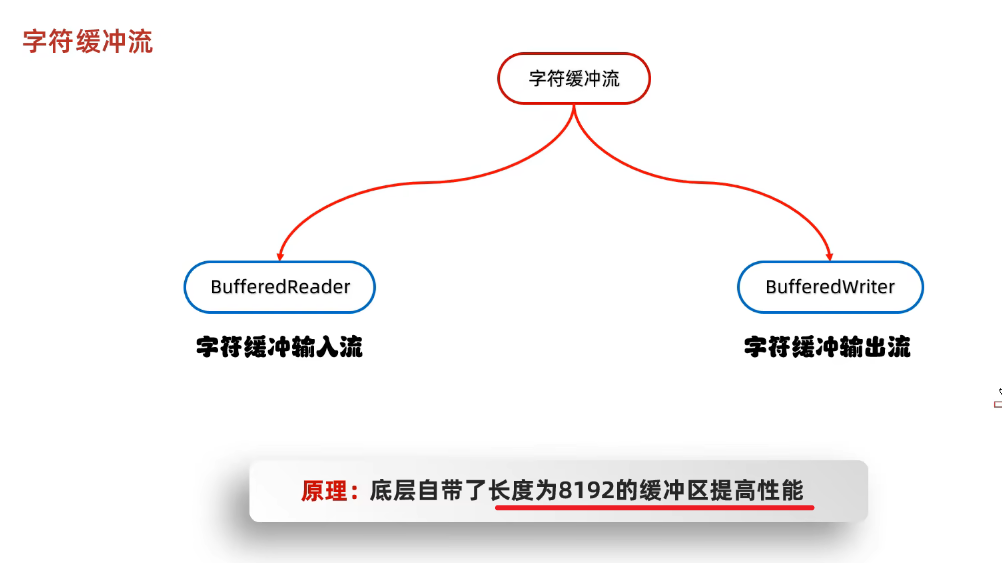
(2)构造方法

(3)特有方法-readLine和newLine
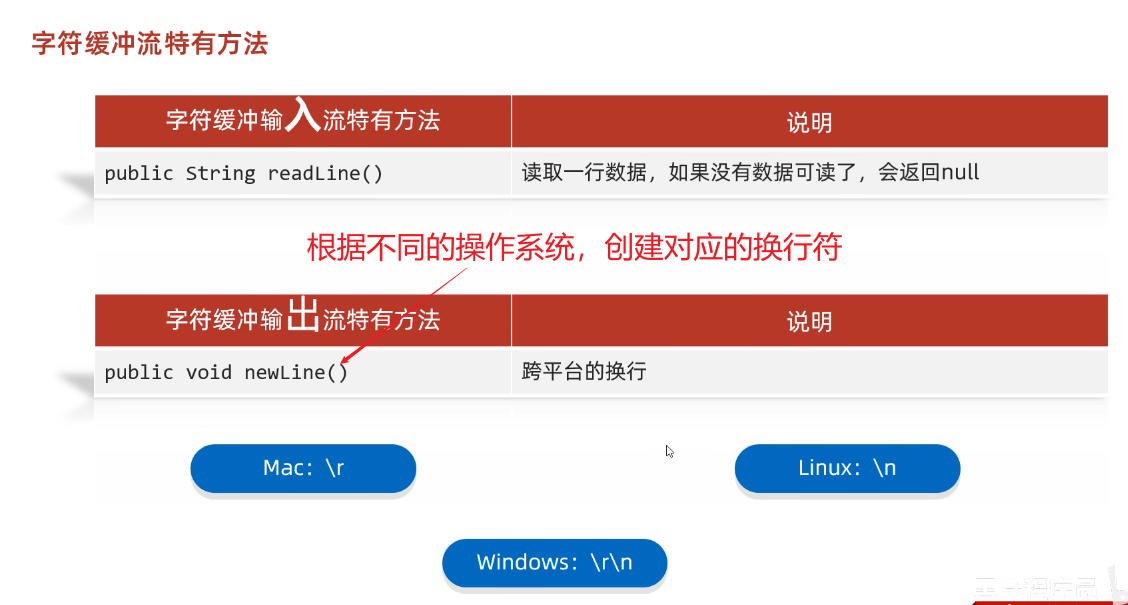
①代码示例-BufferedReader
package com.itheima.mybufferedstream1;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferedStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 字符缓冲输入流:
* 构造方法:
* public BufferedReader(Reader r)
* 特有方法:
* public String readLine() 读一整行
*
* */
//1.创建字符缓冲输入流的对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myio\\a.txt"));
//2.读取数据
//细节:
//readLine方法在读取的时候,一次读一整行,遇到回车换行结束
// 但是他不会把回车换行读到内存当中
/* String line1 = br.readLine();
System.out.println(line1);
String line2 = br.readLine();
System.out.println(line2);*/
String line;
while ((( line = br.readLine()) != null)){
System.out.println(line);
}
//3.释放资源
br.close();
}
}②代码示例-BufferedWriter
package com.itheima.mybufferedstream1;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferedStreamDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
*
* 字符缓冲输出流
* 构造方法:
* public BufferedWriter(Writer r)
* 特有方法:
* public void newLine() 跨平台的换行
*
* */
//1.创建字符缓冲输出流的对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("b.txt",true));
//2.写出数据
bw.write("123");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("456");
bw.newLine();
//3.释放资源
bw.close();
}
}3、总结
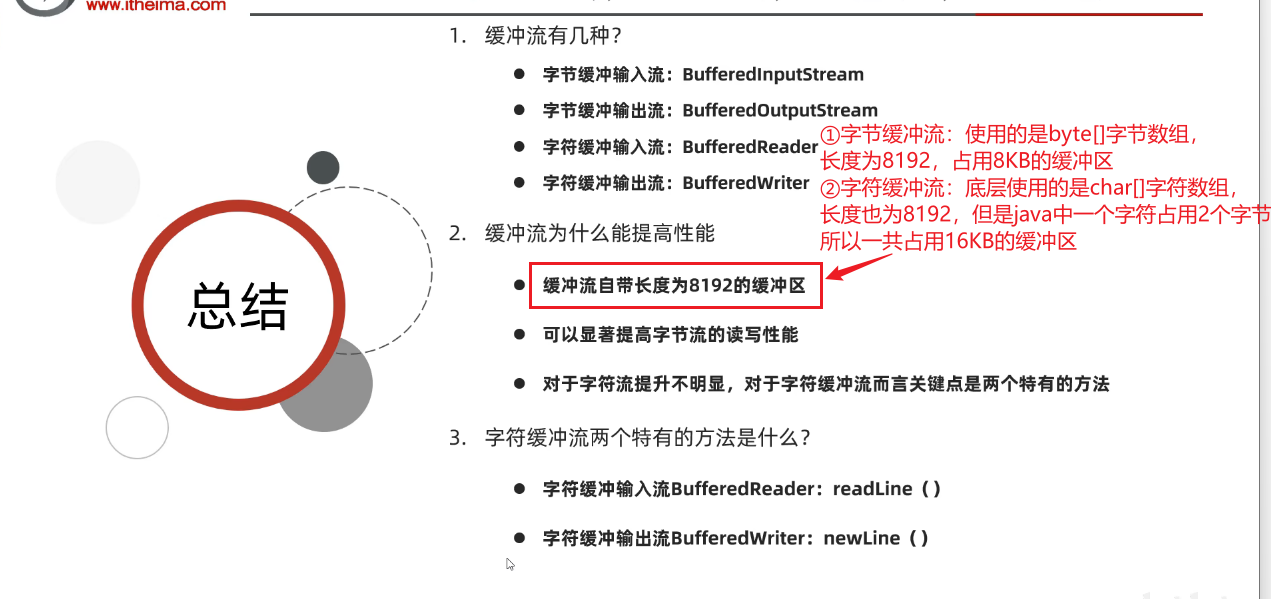
- ①字节缓冲流:使用的是byte[]字节数组,长度为8192,占用8KB的缓冲区
- ②字符缓冲流:底层使用的是char[]字符数组,长度也为8192,但是java中一个字符占用2个字节,所以一共占用16KB的缓冲区
4、综合练习
(1)四种拷贝文件方式-统计用时

package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.*;
public class Test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
四种方式拷贝文件,并统计各自用时
*/
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//method1();
//method2(); //16.253秒
//method3(); //95.466秒
//method4(); //17.686秒
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println((end - start) / 1000.0 + "秒");
}
//字节流的基本流:一次读写一个字节4,588,568,576 字节
public static void method1() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\aaa\\CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1810.iso");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.iso");
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
//字节流的基本流:一次读写一个字节数组
public static void method2() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\aaa\\CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1810.iso");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.iso");
byte[] bytes = new byte[8192];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
//字节流的缓冲流:一次读写一个字节
public static void method3() throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\aaa\\CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1810.iso"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.iso"));
int b;
while ((b = bis.read()) != -1) {
bos.write(b);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
//字节流的缓冲流:一次读写一个字节数组
public static void method4() throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("E:\\aaa\\CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1810.iso"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myio\\copy.iso"));
byte[] bytes = new byte[8192];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}(2)修改文本的顺序


package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class Test06Case01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:把《出师表》的文章顺序进行恢复到一个新文件中。
*/
//1.读取数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myio\\csb.txt"));
String line;
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
list.add(line);
}
br.close();
//2.排序
//排序规则:按照每一行前面的序号进行排列
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
//获取o1和o2的序号
int i1 = Integer.parseInt(o1.split("\\.")[0]);
int i2 = Integer.parseInt(o2.split("\\.")[0]);
return i1 - i2;
}
});
//3.写出
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myio\\result.txt"));
for (String str : list) {
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}改进-使用TreeMap
package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class Test06Case02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:把《出师表》的文章顺序进行恢复到一个新文件中。
*/
//1.读取数据
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myio\\csb.txt"));
String line;
TreeMap<Integer,String> tm = new TreeMap<>();
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
String[] arr = line.split("\\.");
//0:序号 1 :内容
tm.put(Integer.parseInt(arr[0]),line);
}
br.close();
//2.写出数据
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myio\\result2.txt"));
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = tm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
String value = entry.getValue();
bw.write(value);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}(3)软件运行次数

package com.itheima.mytest;
import java.io.*;
public class Test07 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
实现一个验证程序运行次数的小程序,要求如下:
1.当程序运行超过3次时给出提示:本软件只能免费使用3次,欢迎您注册会员后继续使用~
2.程序运行演示如下:
第一次运行控制台输出: 欢迎使用本软件,第1次使用免费~
第二次运行控制台输出: 欢迎使用本软件,第2次使用免费~
第三次运行控制台输出: 欢迎使用本软件,第3次使用免费~
第四次及之后运行控制台输出:本软件只能免费使用3次,欢迎您注册会员后继续使用~
*/
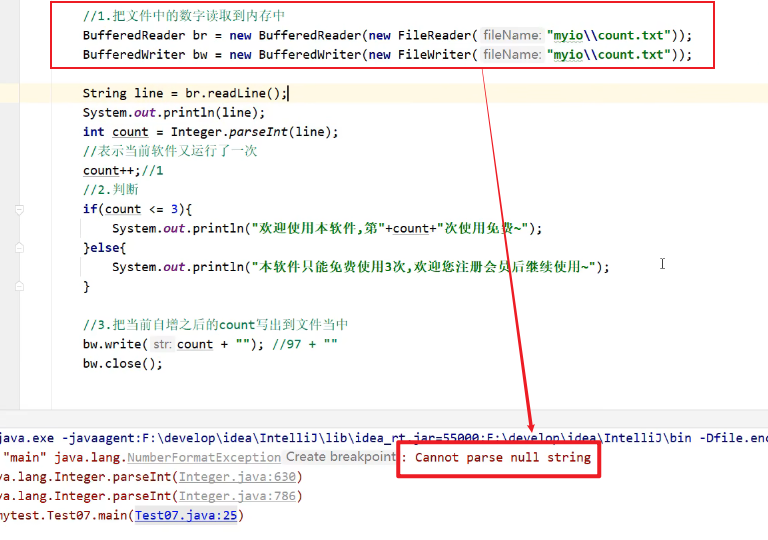
//1.把文件中的数字读取到内存中
//原则:
//IO:随用随创建
// 什么时候不用什么时候关闭
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myio\\count.txt"));
String line = br.readLine();
br.close();
//System.out.println(line);//null
int count = Integer.parseInt(line);
//表示当前软件又运行了一次
count++;//1
//2.判断
if(count <= 3){
System.out.println("欢迎使用本软件,第"+count+"次使用免费~");
}else{
System.out.println("本软件只能免费使用3次,欢迎您注册会员后继续使用~");
}
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myio\\count.txt"));
//3.把当前自增之后的count写出到文件当中
bw.write(count + ""); //97 + ""
bw.close();
}
}十二、IO流的使用原则
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
原则:
- IO原则:
- 随用随创建
- 什么时候不用什么时候关闭
- 原因:由于**输出流默认在写出文件的时候,若文件存在则会清空文件,如果一起创建输入流和输出流的话,会导致读不到数据**。
十三、转换流
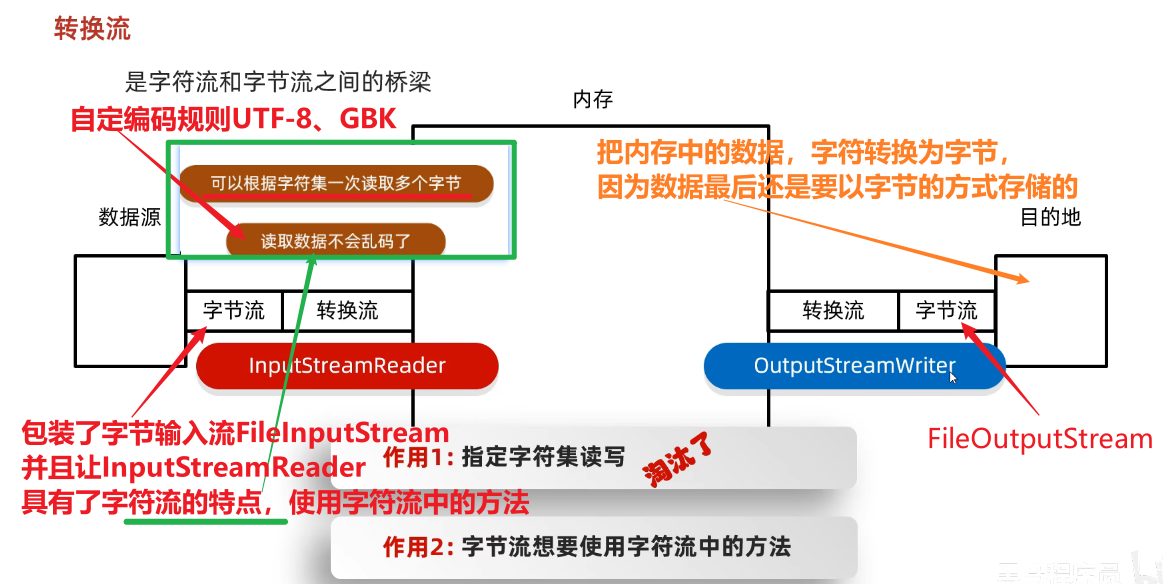
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
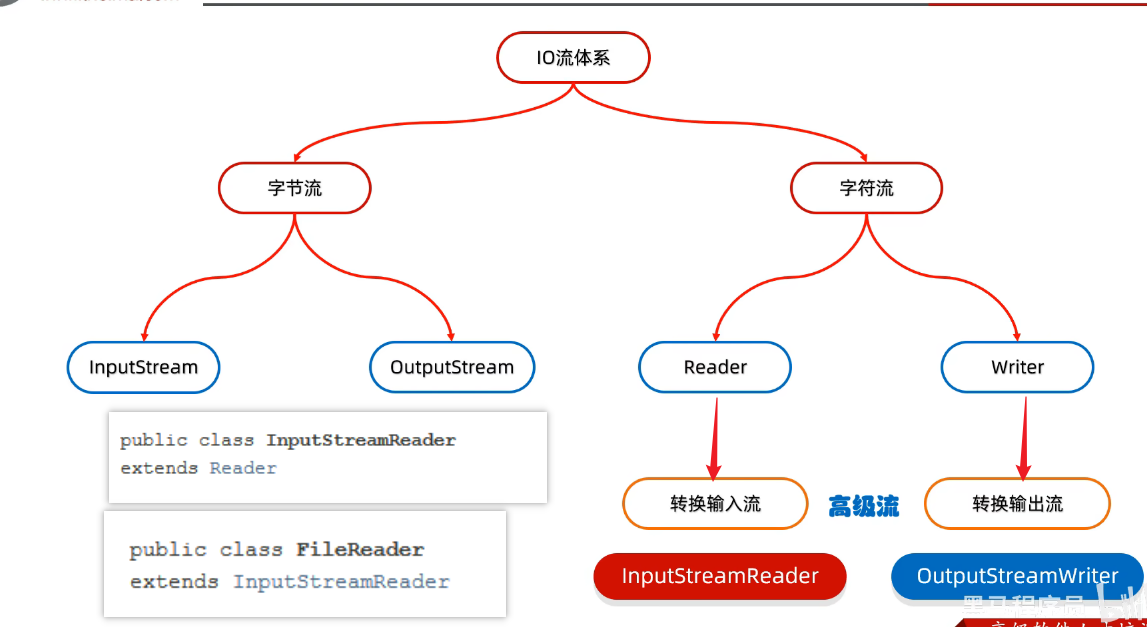
0、转换输入流-InputStreamReader
0、转换输出流-OutputStreamWriter
1、体系
2、概念
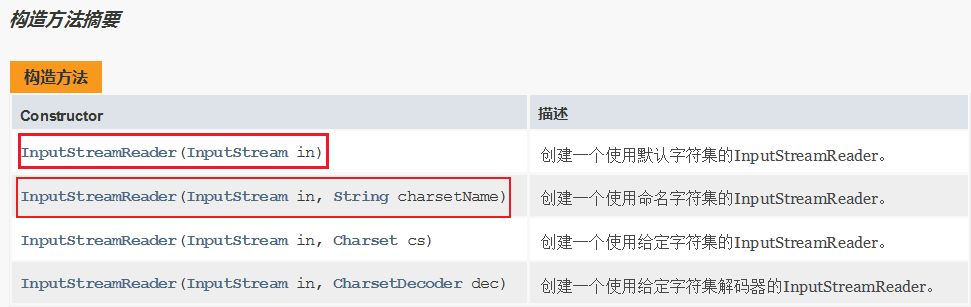
3、构造方法
4、作用1-指定字符集的编码方式
指定读取时
JDK11 以前,使用InputStreamReader指定读取时文件的编码方式
- InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myio\gbkfile.txt"),"GBK");
JDK11 以后,可以这样直接指定读取文件时的编码方式
- FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\gbkfile.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
指定写出时
- JDK11 前
- OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("myio\e.txt"),"UTF-8");
- JDK11 后
- FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\e.txt",Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
- JDK11 前
(1)练习-转换文件编码

①需求1-利用转换流按照指定字符编码读取
package com.itheima.myconvertstream;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class ConvertStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
利用转换流按照指定字符编码读取(了解)
因为JDK11:这种方式被淘汰了。替代方案(掌握)
F:\JavaSE最新版\day29-IO(其他流)\资料\gbkfile.txt
*/
/* //1.创建对象并指定字符编码
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myio\\gbkfile.txt"),"GBK");
//2.读取数据
int ch;
while ((ch = isr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
//3.释放资源
isr.close();*/
//JDK11 以后可以这样直接指定读取文件时的编码方式
FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\gbkfile.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
//2.读取数据
int ch;
while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
//3.释放资源
fr.close();
}
}②需求2-利用转换流按照指定字符编码写出
package com.itheima.myconvertstream;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class ConvertStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
利用转换流按照指定字符编码写出
*/
/*
//1.创建转换流的对象
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("myio\\b.txt"),"GBK");
//2.写出数据
osw.write("你好你好");
//3.释放资源
osw.close();*/
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\c.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
fw.write("你好你好");
fw.close();
}
}③需求3-GBK文件转成UTF-8
package com.itheima.myconvertstream;
import java.io.*;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
public class ConvertStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
将本地文件中的GBK文件,转成UTF-8
*/
//1.JDK11以前的方案
/* InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myio\\b.txt"),"GBK");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("myio\\d.txt"),"UTF-8");
int b;
while((b = isr.read()) != -1){
osw.write(b);
}
osw.close();
isr.close();*/
//2.替代方案
FileReader fr = new FileReader("myio\\b.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("myio\\e.txt",Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
int b;
while ((b = fr.read()) != -1){
fw.write(b);
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}5、作用2-让字节流使用字符流的特有方法
(1)练习-利用字节流每次读取一整行的数据
需求:利用字节流读取文件中的数据,每次读一整行,而且不能出现乱码
- 1.字节流在读取中文的时候,是会出现乱码的,但是字符流可以搞定
- 2.字节流里面是没有读一整行的方法的,只有字符缓冲流才能搞定
解决措施:
3.使用转换流InputStreamReader==包装字节流FileInputStream,让字节流使用字符流的特有方法==
- java
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt"))); String line; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){ System.out.println(line); } br.close();
注意:
用于转换流InputStreamReader包装了字节流FileInputStream*,并且该转换流是属于Reader的字符流,所以他可以让字节流使用字符流的特有方法,比如字符缓存流的读取整行数据readLine()*

①示例代码
package com.itheima.myconvertstream;
import java.io.*;
public class ConvertStreamDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
利用字节流读取文件中的数据,每次读一整行,而且不能出现乱码
//1.字节流在读取中文的时候,是会出现乱码的,但是字符流可以搞定
//2.字节流里面是没有读一整行的方法的,只有字符缓冲流才能搞定
*/
/* FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String str = br.readLine();
System.out.println(str);
br.close();*/
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt")));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
br.close();
}
}6、小结

十四、序列化流
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
0、对象操作输出流-ObjectOutputStream
0、对象操作输入流-ObjectInputStream
1、体系
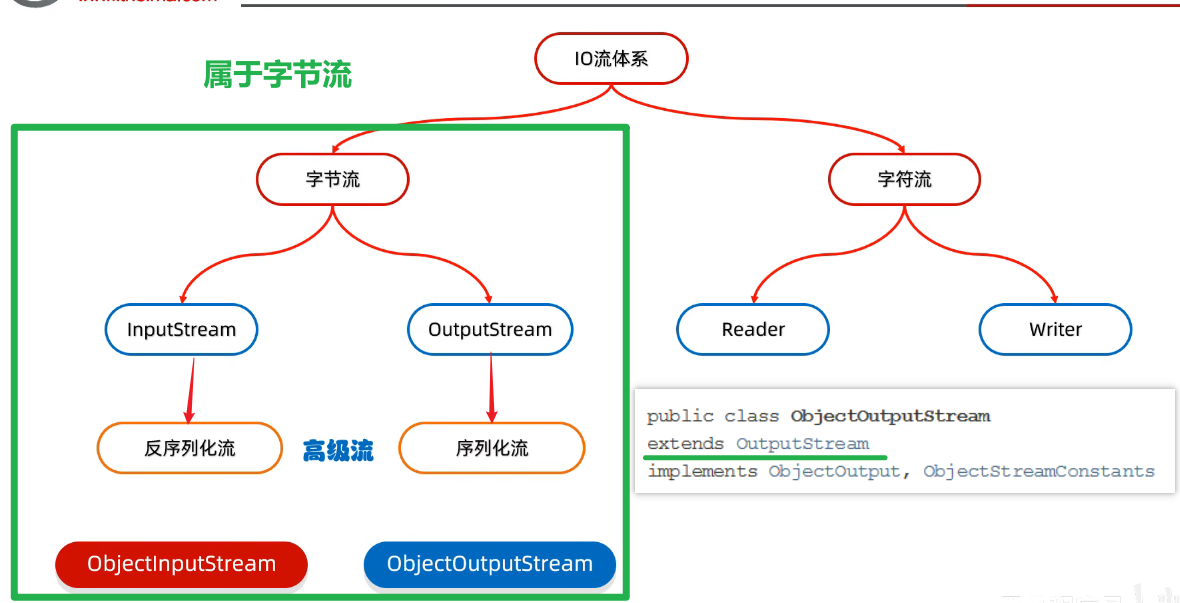
2、序列化流-对象操作输出流
(0)作用

(1)构造方法和成员方法

(2)基本使用
Student对象-实现了Serializable接口
注意
- Serializable接口里面是没有抽象方法,标记型接口,一旦实现了这个接口,那么就表示当前的Student类可以被序列化
package com.itheima.myobjectstream;
import java.io.Serializable;
/*
*
* Serializable接口里面是没有抽象方法,标记型接口
* 一旦实现了这个接口,那么就表示当前的Student类可以被序列化
* 理解:
* 一个物品的合格证
* */
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// set get ...
public String toString() {
return "Student{name = " + name + ", age = " + age + "}";
}
}测试
package com.itheima.myobjectstream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class ObjectStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:
利用序列化流/对象操作输出流,把一个对象写到本地文件中
构造方法:
public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) 把基本流变成高级流
成员方法:
public final void writeObject(Object obj) 把对象序列化(写出)到文件中去
*/
//1.创建对象
Student stu = new Student("zhangsan",23);
//2.创建序列化流的对象/对象操作输出流
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("myio\\a.txt"));
//3.写出数据
oos.writeObject(stu);
//4.释放资源
oos.close();
}
}(3)细节
注意
- Serializable接口里面是没有抽象方法,标记型接口,一旦实现了这个接口,那么就表示当前的Student类可以被序列化
3、反序列化流-对象操作输入流
(0)作用

(1)构造方法和成员方法

(2)基本使用
package com.itheima.myobjectstream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.security.Security;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ObjectStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
/*
需求:
利用反序列化流/对象操作输入流,把文件中中的对象读到程序当中
构造方法:
public ObjectInputStream(InputStream out) 把基本流变成高级流
成员方法:
public Object readObject() 把序列化到本地文件中的对象,读取到程序中来
*/
//1.创建反序列化流的对象
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("myio\\a.txt"));
//2.读取数据
Student o = (Student) ois.readObject();
//3.打印对象
System.out.println(o);
//4.释放资源
ois.close();
}
}4、序列化和反序列化的使用细节

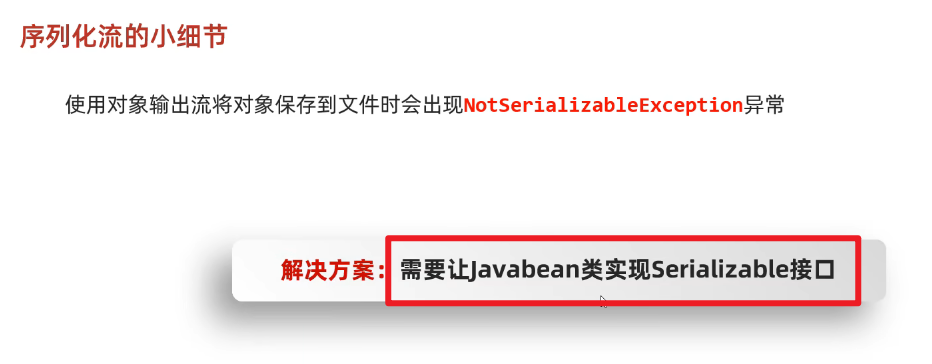
- ①使用序列化流将对象写到文件时,需要让Javabean类实现Serializable接口。否则,会出现NotSerializableException异常
- ②序列化流写到文件中的数据是不能修改的,一旦修改就无法再次读回来了
- ③序列化对象后,修改了Javabean类,再次反序列化,会不会有问题?
- 会出问题,会抛出InvalidclassException异常
- 解决方案:给Javabean类添加serialVersionUID(序列号、版本号)
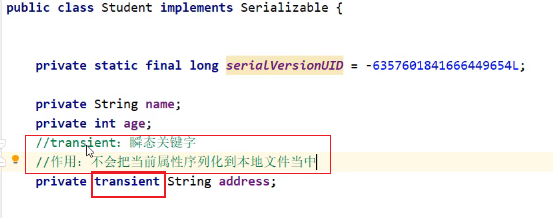
- ④如果一个对象中的某个成员变量的值不想被序列化,又该如何实现呢?
- 解决方案:给该成员变量加瞬态关键字transient关键字修饰,该关键字标记的成员变量不参与序列化过程
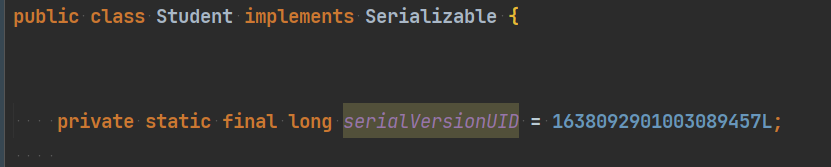
(1)序列号=serialVersionUID
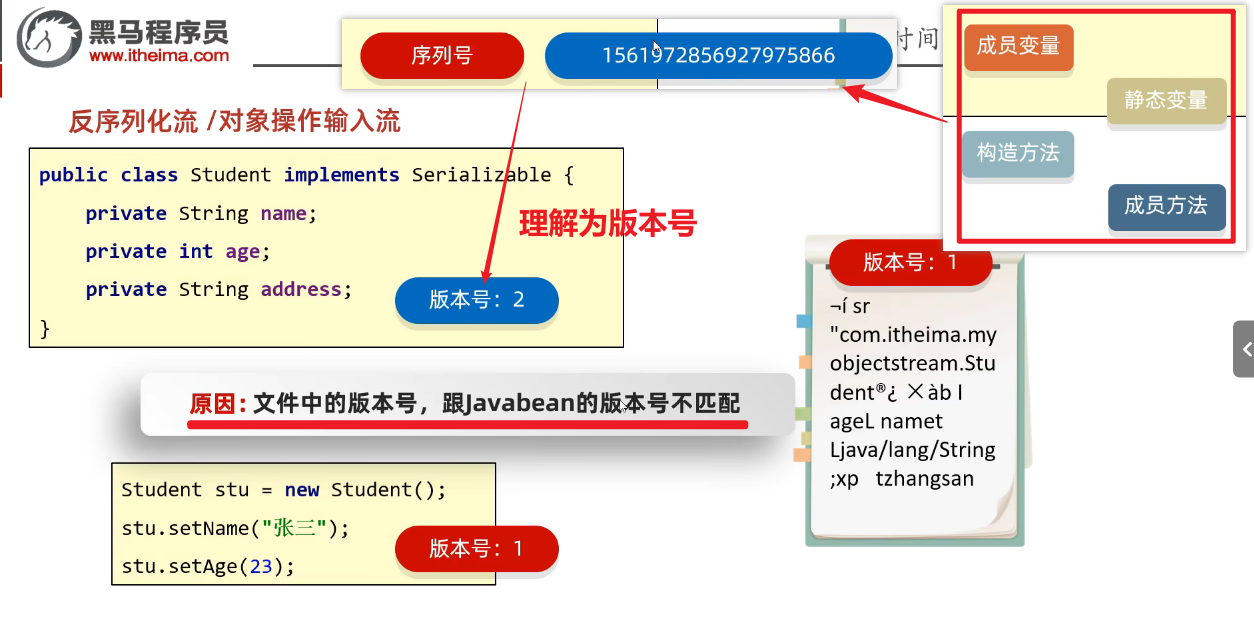
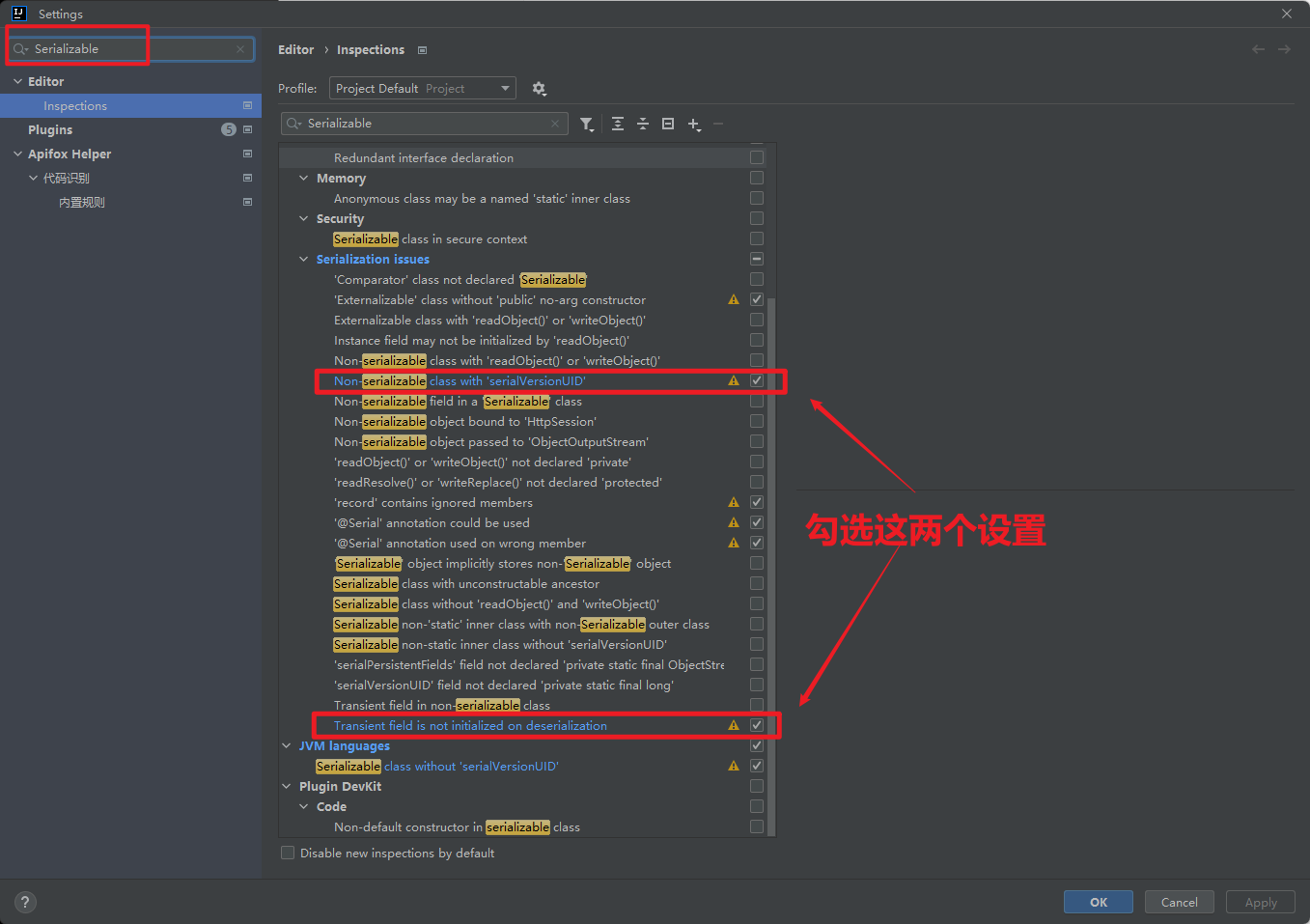
- 序列化ID,如果javabean被序列化了,但是内容变更了(变更时会重新生成序列化id),这个时候再反序列化会报错,所以需要==把序列化ID固定下来==
- IDEA中设置自动提示:再setting中搜索Serializable
- 勾选1:Serializable class without 'serialVersionUID'
- 勾选2:Transient field is not initialized on deserialization
(2)解决保存情况:修改JavaBean类,再次反序列化-指定序列号
序列化对象后,修改了Javabean类,再次反序列化,会不会有问题?
- 会出问题,会抛出InvalidclassException异常
- 解决方案:给Javabean类添加serialVersionUID(序列号、版本号)
IDEA中进行设置
设置后,在每次JavaBean实现了序列化接口Serializable时,会自动提醒程序员需要添加序列号字段serialVersionUID
(3)指定成员变量不被序列化-transient
- 如果一个对象中的某个成员变量的值不想被序列化,又该如何实现呢?
- 解决方案:给该成员变量加瞬态关键字transient关键字修饰,该关键字标记的成员变量不参与序列化过程
5、综合练习-读写多个对象-序列化集合

JavaBean-Student类
package com.pyw.a56objectstream;
import java.io.Serial;
import java.io.Serializable;
/*
Serializable接口没有抽象方法,标记型接口
一但实现了这个接口,表示当前的student类可以被序列化
理解:
一个物品的合格证
*/
public class Student implements Serializable {
/*
序列化ID,如果javabean被序列化了,
但是内容变更了(变更时会重新生成序列化id),这个时候再反序列化会报错
所以需要把序列化ID固定下来
设置自动提示:再setting中搜索Serializable
勾选1:Serializable class without 'serialVersionUID'
勾选2:Transient field is not initialized on deserialization
*/
@Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1714107042296737404L;
private String name;
private int age;
//transient:瞬态关键字:
//作用:不会吧当前属性序列化到本地文件中
private transient String sex;
public Student(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
//set get ...
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}测试
package com.pyw.a56objectstream;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ObjectStreamTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
/*
需求:
将多个自定义对象序列化到文件中,但是对象的个数不确定,如何操作?
多个对象序列化约定:
把多个对象装到一个集合中去,序列化使用这个集合,读取也使用这个集合
*/
//序列化
outputStus();
//反序列化
inputStus();
}
private static void inputStus() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//反序列化stu到程序中
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src/com/pyw/a56objectstream/temp/stus.txt"));
ArrayList students = (ArrayList) ois.readObject();
for (Object student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
ois.close();
}
/**
* 序列化stu到本地
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void outputStus() throws IOException {
//序列化stu到本地
//创建对象
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Student stu1 = new Student("张三",23,"重庆");
Student stu2 = new Student("李四",18,"北碚");
Student stu3 = new Student("王五",19,"万州");
students.add(stu1);
students.add(stu2);
students.add(stu3);
//1、序列化多个对象
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src/com/pyw/a56objectstream/temp/stus.txt"));
//2.放入本地
oos.writeObject(students);
//3.关闭流
oos.close();
}
}十五、打印流
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、体系
2、分类和特点
PrintStream和PrintWriter

3、字节打印流-PrintStream
(1)构造方法

(2)成员方法

(3)示例代码
package com.pyw.a57printstream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class PrintStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
/*
字节打印流:
构造方法
public PrintStream(OutputStream/File/String) 关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径
public PrintStream(String fileName, Charset charset) 指定字符编码
public PrintStream(OutputStreamout, boolean autoFlush) 自动刷新
public PrintStream(OutputStream out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding) 指定字符编码且自动刷新
成员方法:
public void write(int b) 常规方法:规则跟之前一样,将指定的字节写出
public void println(Xxx xx) 特有方法:打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行
public void print(Xxx xx) 特有方法:打印任意数据,不换行
public void printf(String format, Object... args) 特有方法:带有占位符的打印语句,不换行
*/
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("src/com/pyw/a57printstream/temp/print.txt"));
ps.println(97);//原本写出+自动刷新+自动换行
ps.print(true);
ps.println();
// %s: 字符串的占位符
ps.printf("%s 爱上了 %s 在一个有%s的夜晚","阿珍","阿强","流星");
ps.close();
}
}占位符代码示例
package com.pyw.a57printstream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Date;
public class PrintStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("src/com/pyw/a57printstream/temp/占位符.txt");
//% n表示换行
ps.printf("我叫%s %n", "阿玮");
//%s 字符串占位符
ps.printf("%s喜欢%s %n", "阿珍", "阿强");
//%c 把字符变为大写
ps.printf("字母H的大写:%c %n", 'h');
//%b boolean类型占位符
ps.printf("8>3的结果是:%b %n", 8 > 3);
//%d 小数占位符
ps.printf("100的一半是:%d %n", 100 / 2);
ps.printf("100的16进制数是:%x %n", 100);
ps.printf("100的8进制数是:%o %n", 100);
ps.printf("50元的书打8.5折扣是:%f元%n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("计算的结果转16进制:%a %n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("计算的结果转科学计数法表示:%e %n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("计算的结果转成指数和浮点数,结果的长度较短的是:%g %n", 50 * 0.85);
ps.printf("带有百分号的符号表示法,以百分之85为例:%d%% %n", 85);
ps.println("---------------------");
double num1 = 1.0;
ps.printf("num: %.4g %n", num1);
ps.printf("num: %.5g %n", num1);
ps.printf("num: %.6g %n", num1);
float num2 = 1.0F;
ps.printf("num: %.4f %n", num2);
ps.printf("num: %.5f %n", num2);
ps.printf("num: %.6f %n", num2);
ps.println("---------------------");
ps.printf("数字前面带有0的表示方式:%03d %n", 7);
ps.printf("数字前面带有0的表示方式:%04d %n", 7);
ps.printf("数字前面带有空格的表示方式:% 8d %n", 7);
ps.printf("整数分组的效果是:%,d %n", 9989997);
ps.println("---------------------");
//最终结果是10位,小数点后面是5位,不够在前面补空格,补满10位
//如果实际数字小数点后面过长,但是只规定两位,会四舍五入
//如果整数部分过长,超出规定的总长度,会以实际为准
ps.printf("一本书的价格是:%2.5f元%n", 49.8);
ps.printf("%(f%n", -76.04);
//%f,默认小数点后面7位,
//<,表示采取跟前面一样的内容
ps.printf("%f和%3.2f %n", 86.04, 1.789651);
ps.printf("%f和%<3.2f %n", 86.04, 1.789651);
ps.println("---------------------");
Date date = new Date();
// %t 表示时间,但是不能单独出现,要指定时间的格式
// %tc 周二 12月 06 22:08:40 CST 2022
// %tD 斜线隔开
// %tF 冒号隔开(12小时制)
// %tr 冒号隔开(24小时制)
// %tT 冒号隔开(24小时制,带时分秒)
ps.printf("全部日期和时间信息:%tc %n", date);
ps.printf("月/日/年格式:%tD %n", date);
ps.printf("年-月-日格式:%tF %n", date);
ps.printf("HH:MM:SS PM格式(12时制):%tr %n", date);
ps.printf("HH:MM格式(24时制):%tR %n", date);
ps.printf("HH:MM:SS格式(24时制):%tT %n", date);
System.out.println("---------------------");
ps.printf("星期的简称:%ta %n", date);
ps.printf("星期的全称:%tA %n", date);
ps.printf("英文月份简称:%tb %n", date);
ps.printf("英文月份全称:%tB %n", date);
ps.printf("年的前两位数字(不足两位前面补0):%tC %n", date);
ps.printf("年的后两位数字(不足两位前面补0):%ty %n", date);
ps.printf("一年中的第几天:%tj %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的月份(不足两位前面补0):%tm %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的日(不足两位前面补0):%td %n", date);
ps.printf("月份的日(前面不补0):%te %n", date);
System.out.println("---------------------");
ps.printf("两位数字24时制的小时(不足2位前面补0):%tH %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字12时制的小时(不足2位前面补0):%tI %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字24时制的小时(前面不补0):%tk %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字12时制的小时(前面不补0):%tl %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的分钟(不足2位前面补0):%tM %n", date);
ps.printf("两位数字的秒(不足2位前面补0):%tS %n", date);
ps.printf("三位数字的毫秒(不足3位前面补0):%tL %n", date);
ps.printf("九位数字的毫秒数(不足9位前面补0):%tN %n", date);
ps.printf("小写字母的上午或下午标记(英):%tp %n", date);
ps.printf("小写字母的上午或下午标记(中):%tp %n", date);
ps.printf("相对于GMT的偏移量:%tz %n", date);
ps.printf("时区缩写字符串:%tZ%n", date);
ps.printf("1970-1-1 00:00:00 到现在所经过的秒数:%ts %n", date);
ps.printf("1970-1-1 00:00:00 到现在所经过的毫秒数:%tQ %n", date);
ps.close();
}
}4、字符打印流-PrintWriter
(1)构造方法

(2)成员方法

(3)示例代码
package com.itheima.myprintstream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class PrintStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
字符打印流:
构造方法
public PrintWriter(Write/File/String) 关联字节输出流/文件/文件路径
public PrintWriter(String fileName, Charset charset) 指定字符编码
public PrintWriter(Write, boolean autoFlush) 自动刷新
public PrintWriter(Write out, boolean autoFlush, String encoding) 指定字符编码且自动刷新
成员方法:
public void write(int b) 常规方法:规则跟之前一样,将指定的字节写出
public void println(Xxx xx) 特有方法:打印任意数据,自动刷新,自动换行
public void print(Xxx xx) 特有方法:打印任意数据,不换行
public void printf(String format, Object... args) 特有方法:带有占位符的打印语句,不换行
*/
//1.创建字符打印流的对象
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("myio\\a.txt"),true);
//2.写出数据
pw.println("今天你终于叫我名字了,虽然叫错了,但是没关系,我马上改");
pw.print("你好你好");
pw.printf("%s爱上了%s","阿珍","阿强");
//3.释放资源
pw.close();
}
}(4)标准输出流-System.out.print()
- 获取打印流的对象,此打印流在虚拟机启动的时候,由虚拟机创建,默认指向控制台
- 特殊的打印流,系统中的标准输出流,是不能关闭,在系统中是唯一的.
- System.out.println("456");
- PrintStream ps = System.out;
- ps.println("123");
- System.out.println("456");
package com.itheima.myprintstream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class PrintStreamDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 打印流的应用场景
* */
//获取打印流的对象,此打印流在虚拟机启动的时候,由虚拟机创建,默认指向控制台
//特殊的打印流,系统中的标准输出流,是不能关闭,在系统中是唯一的。
PrintStream ps = System.out;
//调用打印流中的方法println
//写出数据,自动换行,自动刷新
ps.println("123");
//ps.close();
ps.println("你好你好");
System.out.println("456");
}
}5、总结

十六、解压缩流/压缩流
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、体系
2、解压缩流-ZipInputStream
(1)概念

(2)代码示例-解压缩
- 解压的本质:把压缩包里面的每一个文件或者文件夹读取出来,按照层级拷贝到目的地当中。
- 创建一个解压缩流用来读取压缩包中的数据
package com.itheima.myzipstream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipInputStream;
/*
* 解压缩流
*
* */
public class ZipStreamDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建一个File表示要解压的压缩包
File src = new File("D:\\aaa.zip");
//2.创建一个File表示解压的目的地
File dest = new File("D:\\");
//调用方法
unzip(src,dest);
}
//定义一个方法用来解压
public static void unzip(File src,File dest) throws IOException {
//解压的本质:把压缩包里面的每一个文件或者文件夹读取出来,按照层级拷贝到目的地当中
//创建一个解压缩流用来读取压缩包中的数据
ZipInputStream zip = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
//要先获取到压缩包里面的每一个zipentry对象
//表示当前在压缩包中获取到的文件或者文件夹
ZipEntry entry;
while((entry = zip.getNextEntry()) != null){
System.out.println(entry);
if(entry.isDirectory()){
//文件夹:需要在目的地dest处创建一个同样的文件夹
File file = new File(dest,entry.toString());
file.mkdirs();
}else{
//文件:需要读取到压缩包中的文件,并把他存放到目的地dest文件夹中(按照层级目录进行存放)
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,entry.toString()));
int b;
while((b = zip.read()) != -1){
//写到目的地
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
//表示在压缩包中的一个文件处理完毕了。
zip.closeEntry();
}
}
zip.close();
}
}3、压缩流-ZipOutputStream
(1)概念

(2)示例代码-压缩单个文件
package com.itheima.myzipstream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class ZipStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 压缩流
* 需求:
* 把D:\\a.txt打包成一个压缩包
* */
//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件
File src = new File("D:\\a.txt");
//2.创建File对象表示压缩包的位置
File dest = new File("D:\\");
//3.调用方法用来压缩
toZip(src,dest);
}
/*
* 作用:压缩
* 参数一:表示要压缩的文件
* 参数二:表示压缩包的位置
* */
public static void toZip(File src,File dest) throws IOException {
//1.创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(new File(dest,"a.zip")));
//2.创建ZipEntry对象,表示压缩包里面的每一个文件和文件夹
//参数:压缩包里面的路径
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry("aaa\\bbb\\a.txt");
//3.把ZipEntry对象放到压缩包当中
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//4.把src文件中的数据写到压缩包当中
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src);
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1){
zos.write(b);
}
zos.closeEntry();
zos.close();
}
}(3)示例代码-压缩文件夹
package com.itheima.myzipstream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.zip.ZipEntry;
import java.util.zip.ZipOutputStream;
public class ZipStreamDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
* 压缩流
* 需求:
* 把D:\\aaa文件夹压缩成一个压缩包
* */
//1.创建File对象表示要压缩的文件夹
File src = new File("D:\\aaa");
//2.创建File对象表示压缩包放在哪里(压缩包的父级路径)
File destParent = src.getParentFile();//D:\\
//3.创建File对象表示压缩包的路径
File dest = new File(destParent,src.getName() + ".zip");
//4.创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zos = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dest));
//5.获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
toZip(src,zos,src.getName());//aaa
//6.释放资源
zos.close();
}
/*
* 作用:获取src里面的每一个文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
* 参数一:数据源
* 参数二:压缩流
* 参数三:压缩包内部的路径
* */
public static void toZip(File src,ZipOutputStream zos,String name) throws IOException {
//1.进入src文件夹
File[] files = src.listFiles();
//2.遍历数组
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
//3.判断-文件,变成ZipEntry对象,放入到压缩包当中
ZipEntry entry = new ZipEntry(name + "\\" + file.getName());// aaa\\no1\\a.txt
zos.putNextEntry(entry);
//读取文件中的数据,写到压缩包
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int b;
while((b = fis.read()) != -1){
zos.write(b);
}
fis.close();
zos.closeEntry();
}else{
//4.判断-文件夹,递归
toZip(file,zos,name + "\\" + file.getName());
// no1 aaa \\ no1
}
}
}
}十七、工具类-Commons-io
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟


1、使用步骤-导入到Java项目中

2、常见方法
(1)文件/文件夹相关
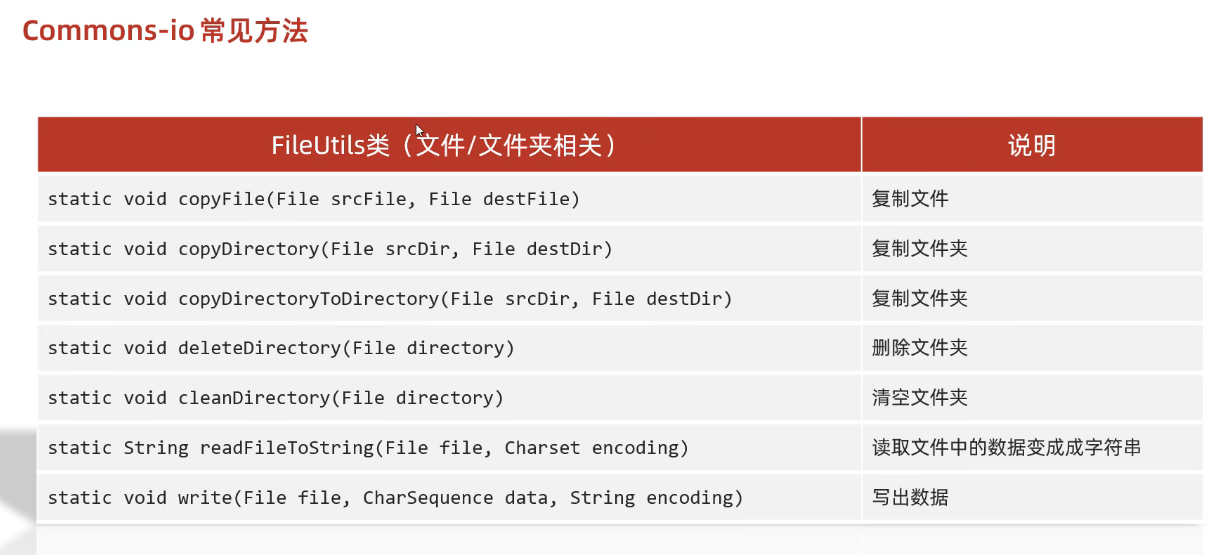
(2)流相关

(3)示例代码-FileUtils
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class FileUtilsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 复制文件
File srcFile = new File("source.txt");
File destFile = new File("destination.txt");
FileUtils.copyFile(srcFile, destFile);
// 复制文件夹
File srcDir = new File("srcFolder");
File destDir = new File("destFolder");
FileUtils.copyDirectory(srcDir, destDir);
// 复制文件夹到另一个文件夹
FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(srcDir, new File("parentFolder"));
// 删除文件夹
FileUtils.deleteDirectory(new File("folderToDelete"));
// 清空文件夹
FileUtils.cleanDirectory(new File("folderToClean"));
// 读取文件内容为字符串
String content = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File("readme.txt"), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(content);
// 写出数据到文件
FileUtils.write(new File("output.txt"), "Hello, FileUtils!", "UTF-8");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}(4)示例代码-IOUtils
import org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils;
import java.io.*;
public class IOUtilsExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 复制文件(InputStream -> OutputStream)
try (InputStream input = new FileInputStream("source.txt");
OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream("copy.txt")) {
IOUtils.copy(input, output);
}
// 复制大文件(Reader -> Writer)
try (Reader reader = new FileReader("largeFile.txt");
Writer writer = new FileWriter("copyLarge.txt")) {
IOUtils.copyLarge(reader, writer);
}
// 读取文件内容为字符串
try (Reader reader = new FileReader("data.txt")) {
String content = IOUtils.toString(reader);
System.out.println(content);
}
// 写出数据到 OutputStream
try (OutputStream output = new FileOutputStream("output.txt")) {
IOUtils.write("Hello, IOUtils!", output, "UTF-8");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}十八、==Hutool==工具包
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
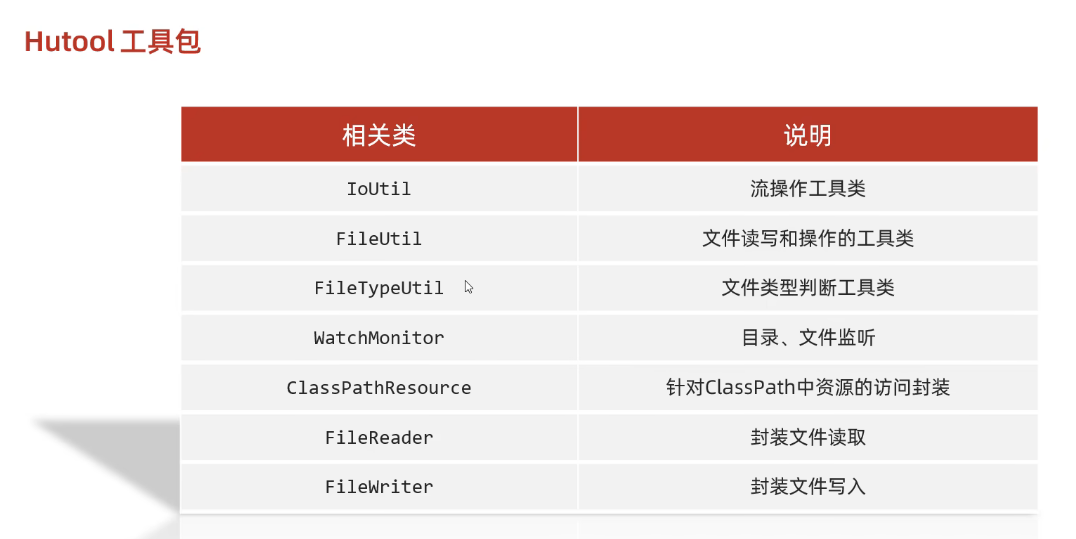
1、代码示例
package com.itheima.myhutool;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
import java.util.List;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
FileUtil类:
file:根据参数创建一个file对象
touch:根据参数创建文件
writeLines:把集合中的数据写出到文件中,覆盖模式。
appendLines:把集合中的数据写出到文件中,续写模式。
readLines:指定字符编码,把文件中的数据,读到集合中。
readUtf8Lines:按照UTF-8的形式,把文件中的数据,读到集合中
copy:拷贝文件或者文件夹
*/
/* File file1 = FileUtil.file("D:\\", "aaa", "bbb", "a.txt");
System.out.println(file1);//D:\aaa\bbb\a.txt
File touch = FileUtil.touch(file1);
System.out.println(touch);
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
File file2 = FileUtil.writeLines(list, "D:\\a.txt", "UTF-8");
System.out.println(file2);*/
/* ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
File file3 = FileUtil.appendLines(list, "D:\\a.txt", "UTF-8");
System.out.println(file3);*/
List<String> list = FileUtil.readLines("D:\\a.txt", "UTF-8");
System.out.println(list);
}
}十九、IO综合练习
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、制造假数据-爬取数据

package com.itheima.myiotest1;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLConnection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
制造假数据:
获取姓氏:https://hanyu.baidu.com/shici/detail?pid=0b2f26d4c0ddb3ee693fdb1137ee1b0d&from=kg0
获取男生名字:http://www.haoming8.cn/baobao/10881.html
获取女生名字:http://www.haoming8.cn/baobao/7641.html
*/
//1.定义变量记录网址
String familyNameNet = "https://hanyu.baidu.com/shici/detail?pid=0b2f26d4c0ddb3ee693fdb1137ee1b0d&from=kg0";
String boyNameNet = "http://www.haoming8.cn/baobao/10881.html";
String girlNameNet = "http://www.haoming8.cn/baobao/7641.html";
//2.爬取数据,把网址上所有的数据拼接成一个字符串
String familyNameStr = webCrawler(familyNameNet);
String boyNameStr = webCrawler(boyNameNet);
String girlNameStr = webCrawler(girlNameNet);
//3.通过正则表达式,把其中符合要求的数据获取出来
ArrayList<String> familyNameTempList = getData(familyNameStr,"(.{4})(,|。)",1);
ArrayList<String> boyNameTempList = getData(boyNameStr,"([\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]{2})(、|。)",1);
ArrayList<String> girlNameTempList = getData(girlNameStr,"(.. ){4}..",0);
//4.处理数据
//familyNameTempList(姓氏)
//处理方案:把每一个姓氏拆开并添加到一个新的集合当中
ArrayList<String> familyNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : familyNameTempList) {
//str 赵钱孙李 周吴郑王 冯陈褚卫 蒋沈韩杨
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
familyNameList.add(c + "");
}
}
//boyNameTempList(男生的名字)
//处理方案:去除其中的重复元素
ArrayList<String> boyNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : boyNameTempList) {
if(!boyNameList.contains(str)){
boyNameList.add(str);
}
}
//Stream流-去重
//List<String> boyNameList = boyNameTempList.stream().distinct().toList();
//System.out.println("男生名集合:" + boyNameList);
//girlNameTempList(女生的名字)
//处理方案:把里面的每一个元素用空格进行切割,得到每一个女生的名字
ArrayList<String> girlNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : girlNameTempList) {
String[] arr = str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
girlNameList.add(arr[i]);
}
}
//5.生成数据
//姓名(唯一)-性别-年龄
ArrayList<String> list = getInfos(familyNameList, boyNameList, girlNameList, 70, 50);
Collections.shuffle(list);
//6.写出数据
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myiotest\\names.txt"));
for (String str : list) {
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
/*
* 作用:
* 获取男生和女生的信息:张三-男-23
*
* 形参:
* 参数一:装着姓氏的集合
* 参数二:装着男生名字的集合
* 参数三:装着女生名字的集合
* 参数四:男生的个数
* 参数五:女生的个数
* */
public static ArrayList<String> getInfos(ArrayList<String> familyNameList,ArrayList<String> boyNameList,ArrayList<String> girlNameList, int boyCount,int girlCount){
//1.生成男生不重复的名字
HashSet<String> boyhs = new HashSet<>();
while (true){
if(boyhs.size() == boyCount){
break;
}
//随机
Collections.shuffle(familyNameList);
Collections.shuffle(boyNameList);
boyhs.add(familyNameList.get(0) + boyNameList.get(0));
}
//2.生成女生不重复的名字
HashSet<String> girlhs = new HashSet<>();
while (true){
if(girlhs.size() == girlCount){
break;
}
//随机
Collections.shuffle(familyNameList);
Collections.shuffle(girlNameList);
girlhs.add(familyNameList.get(0) + girlNameList.get(0));
}
//3.生成男生的信息并添加到集合当中
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Random r = new Random();
//【18 ~ 27】
for (String boyName : boyhs) {
//boyName依次表示每一个男生的名字
int age = r.nextInt(10) + 18;
list.add(boyName + "-男-" + age);
}
//4.生成女生的信息并添加到集合当中
//【18 ~ 25】
for (String girlName : girlhs) {
//girlName依次表示每一个女生的名字
int age = r.nextInt(8) + 18;
list.add(girlName + "-女-" + age);
}
return list;
}
/*
* 作用:根据正则表达式获取字符串中的数据
* 参数一:
* 完整的字符串
* 参数二:
* 正则表达式
* 参数三:
* 获取数据
* 0:获取符合正则表达式所有的内容
* 1:获取正则表达式中第一组数据
* 2:获取正则表达式中第二组数据
* ...以此类推
*
* 返回值:
* 真正想要的数据
*
* */
private static ArrayList<String> getData(String str, String regex,int index) {
//1.创建集合存放数据
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
//2.按照正则表达式的规则,去获取数据
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
//按照pattern的规则,到str当中获取数据
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(str);
while (matcher.find()){
list.add(matcher.group(index)); //获取组别group的index
}
return list;
}
/*
* 作用:
* 从网络中爬取数据,把数据拼接成字符串返回
* 形参:
* 网址
* 返回值:
* 爬取到的所有数据
* */
public static String webCrawler(String net) throws IOException {
//1.定义StringBuilder拼接爬取到的数据
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//2.创建一个URL对象
URL url = new URL(net);
//3.链接上这个网址
//细节:保证网络是畅通的,而且这个网址是可以链接上的。
URLConnection conn = url.openConnection();
//4.读取数据
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream());
int ch;
while ((ch = isr.read()) != -1){
sb.append((char)ch);
}
//5.释放资源
isr.close();
//6.把读取到的数据返回
return sb.toString();
}
}2、使用Hutool工具包制造假数据
package com.itheima.myiotest1;
import cn.hutool.core.io.FileUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.util.ReUtil;
import cn.hutool.http.HttpUtil;
import java.util.*;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//利用糊涂包生成假数据,并写到文件当中
//1. 定义网址
String familyNameNet = "https://hanyu.baidu.com/shici/detail?pid=0b2f26d4c0ddb3ee693fdb1137ee1b0d&from=kg0";
String boyNameNet = "http://www.haoming8.cn/baobao/10881.html";
String girlNameNet = "http://www.haoming8.cn/baobao/7641.html";
//2.爬取数据
String familyNameStr = HttpUtil.get(familyNameNet);
String boyNameStr = HttpUtil.get(boyNameNet);
String girlNameStr = HttpUtil.get(girlNameNet);
//3.利用正则表达式获取数据
//通过正则表达式,把其中符合要求的数据获取出来
List<String> familyNameTempList = ReUtil.findAll("(.{4})(,|。)", familyNameStr, 1);
List<String> boyNameTempList = ReUtil.findAll("([\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]{2})(、|。)", boyNameStr, 1);
List<String> girlNameTempList = ReUtil.findAll("(.. ){4}..", girlNameStr, 0);
System.out.println(familyNameTempList);
System.out.println(boyNameTempList);
System.out.println(girlNameTempList);
//4.处理数据
//familyNameTempList(姓氏)
//处理方案:把每一个姓氏拆开并添加到一个新的集合当中
ArrayList<String> familyNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : familyNameTempList) {
//str 赵钱孙李 周吴郑王 冯陈褚卫 蒋沈韩杨
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char c = str.charAt(i);
familyNameList.add(c + "");
}
}
//boyNameTempList(男生的名字)
//处理方案:去除其中的重复元素
ArrayList<String> boyNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : boyNameTempList) {
if(!boyNameList.contains(str)){
boyNameList.add(str);
}
}
//girlNameTempList(女生的名字)
//处理方案:把里面的每一个元素用空格进行切割,得到每一个女生的名字
ArrayList<String> girlNameList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String str : girlNameTempList) {
String[] arr = str.split(" ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
girlNameList.add(arr[i]);
}
}
//5.生成数据
//姓名(唯一)-性别-年龄
ArrayList<String> list = getInfos(familyNameList, boyNameList, girlNameList, 70, 50);
Collections.shuffle(list);
//6.写出数据
//细节:
//糊涂包的相对路径,不是相对于当前项目而言的,而是相对class文件而言的
FileUtil.writeLines(list,"D:\\names.txt","UTF-8");
}
/*
* 作用:
* 获取男生和女生的信息:张三-男-23
*
* 形参:
* 参数一:装着姓氏的集合
* 参数二:装着男生名字的集合
* 参数三:装着女生名字的集合
* 参数四:男生的个数
* 参数五:女生的个数
* */
public static ArrayList<String> getInfos(ArrayList<String> familyNameList,ArrayList<String> boyNameList,ArrayList<String> girlNameList, int boyCount,int girlCount){
//1.生成男生不重复的名字
HashSet<String> boyhs = new HashSet<>();
while (true){
if(boyhs.size() == boyCount){
break;
}
//随机
Collections.shuffle(familyNameList);
Collections.shuffle(boyNameList);
boyhs.add(familyNameList.get(0) + boyNameList.get(0));
}
//2.生成女生不重复的名字
HashSet<String> girlhs = new HashSet<>();
while (true){
if(girlhs.size() == girlCount){
break;
}
//随机
Collections.shuffle(familyNameList);
Collections.shuffle(girlNameList);
girlhs.add(familyNameList.get(0) + girlNameList.get(0));
}
//3.生成男生的信息并添加到集合当中
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Random r = new Random();
//【18 ~ 27】
for (String boyName : boyhs) {
//boyName依次表示每一个男生的名字
int age = r.nextInt(10) + 18;
list.add(boyName + "-男-" + age);
}
//4.生成女生的信息并添加到集合当中
//【18 ~ 25】
for (String girlName : girlhs) {
//girlName依次表示每一个女生的名字
int age = r.nextInt(8) + 18;
list.add(girlName + "-女-" + age);
}
return list;
}
}3、随机点名器
(1)随机点名器-1

文件
钦逸抒-女-21
屈燕妮-女-24
阴诗雁-女-25
伯荷燕-女-24
欧文新-男-20
董泽欧-男-18
滕星磊-男-18
阚晴岚-女-22
傅彬远-男-19
左花依-女-24
鱼德合-男-24
巫依珍-女-18
里柏新-男-25
利棕德-男-25
冶德合-男-19
喻雪慧-女-20
庞庆云-男-22
甘亦曼-女-19
微安筠-女-25
向瀚德-男-24代码
package com.itheima.myiotest2;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Random;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*需求:
需求:
有一个文件里面存储了班级同学的信息,每一个信息占一行。
格式为:张三-男-23
要求通过程序实现随机点名器。
运行效果:
第一次运行程序:随机同学姓名1(只显示名字)
第二次运行程序:随机同学姓名2(只显示名字)
第三次运行程序:随机同学姓名3(只显示名字)
…
*/
//1.读取文件中学生的姓名
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest2\\names.txt"));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
list.add(line);
}
br.close();
//2.随机抽取(解法一)
Random r = new Random();
int index = r.nextInt(list.size());
String randomName1 = list.get(index);
String[] arr1 = randomName1.split("-");
System.out.println(arr1[0]);
//2.随机抽取(解法二)
Collections.shuffle(list);
String randomName2 = list.get(0);
String[] arr2 = randomName2.split("-");
System.out.println(arr2[0]);
}
}(2)随机点名器-作弊功能

package com.itheima.myiotest4;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*需求:
一个文件里面存储了班级同学的姓名,每一个姓名占一行。
要求通过程序实现随机点名器。
第三次必定是张三同学
运行效果:
第一次运行程序:随机同学姓名1
第二次运行程序:随机同学姓名2
第三次运行程序:张三
…
*/
//1.读取数据,并把学生信息添加到集合当中
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest4\\names.txt"));
String line;
while ((line = br1.readLine()) != null){
list.add(line);
}
br1.close();
//2.读取当前程序已经运行的次数
BufferedReader br2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest4\\count.txt"));
String countStr = br2.readLine();
int count = Integer.parseInt(countStr);
br2.close();
//4.表示程序再次运行了一次
count++;
//3.判断,如果当前已经是第三次,直接打印,不是第三次才随机
if(count == 3){
System.out.println("张三");
}else {
Collections.shuffle(list);
String stuInfo = list.get(0);
System.out.println(stuInfo);
}
//4.将程序已经运行的次数写会本地文件
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest4\\count.txt"));
bw.write(count + "");
bw.close();
}
}随机点名器-不重复点名

package com.itheima.myiotest5;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*需求:
一个文件里面存储了班级同学的姓名,每一个姓名占一行。
要求通过程序实现随机点名器。
运行结果要求:
被点到的学生不会再被点到。
但是如果班级中所有的学生都点完了, 需要重新开启第二轮点名。
核心思想:
点一个删一个,把删除的备份,全部点完时还原数据。
*/
//1.定义变量,表示初始文件路径,文件中存储所有的学生信息
String src = "myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest5\\names.txt";
//2.定义变量,表示备份文件,一开始文件为空
String backups = "myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest5\\backups.txt";
//3.读取初始文件中的数据,并把学生信息添加到集合当中
ArrayList<String> list = readFile(src);
//4.判断集合中是否有数据
if (list.size() == 0) {
//5.如果没有数据,表示所有学生已经点完,从backups.txt中还原数据即可
//还原数据需要以下步骤:
//5.1 读取备份文件中所有的数据
list = readFile(backups);
//5.2 把所有的数据写到初始文件中
writeFile(src, list, false);
//5.3 删除备份文件
new File(backups).delete();
}
//5.集合中有数据,表示还没有点完,点一个删一个,把删除的备份到backups.txt当中
//打乱集合
Collections.shuffle(list);
//获取0索引的学生信息并删除
String stuInfo = list.remove(0);
//打印随机到的学生信息
System.out.println("当前被点到的学生为:" + stuInfo);
//把删除之后的所有学生信息,写到初始文件中
writeFile(src, list, false);
//把删除的学生信息备份(追加写入)
writeFile(backups, stuInfo, true);
}
private static void writeFile(String pathFile, ArrayList<String> list, boolean isAppend) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(pathFile, isAppend));
for (String str : list) {
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
private static void writeFile(String pathFile, String str, boolean isAppend) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(pathFile, isAppend));
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.close();
}
private static ArrayList<String> readFile(String pathFile) throws IOException {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(pathFile));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
list.add(line);
}
br.close();
return list;
}
}(6)随机点名器-指定概率

package com.itheima.myiotest3;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Random;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*需求:
一个文件里面存储了班级同学的信息,格式为:张三-男-23
每一个学生信息占一行。
要求通过程序实现随机点名器。
70%的概率随机到男生
30%的概率随机到女生
随机100万次,统计结果。看生成男生和女生的比例是不是接近于7:3
*/
//1.读取数据,并把男生和女生的信息添加到不同的集合当中
ArrayList<String> boyNameList = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> girlNameList = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest3\\names.txt"));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
String[] arr = line.split("-");
if(arr[1].equals("男")){
boyNameList.add(line);
}else{
girlNameList.add(line);
}
}
br.close();
//2.定义权重集合,男女比例:7:3
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0); //这里只有两种,男女,若是有很多种的话,可以考虑使用第二种随机权重算法
//3.定义变量,统计被点到的次数
int boyCount = 0;
int girlCount = 0;
Random r = new Random();
//4.循环100万次
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
//5.从权重集合中获取随机数据
int index = r.nextInt(list.size());
int weight = list.get(index);
//6.判断获取的随机数据是1还是0
if(weight == 1){
//1就随机男生
Collections.shuffle(boyNameList);
String boyInfo = boyNameList.get(0);
System.out.println(boyInfo);
boyCount++;
}else{
//0就随机女生
Collections.shuffle(girlNameList);
String girlInfo = girlNameList.get(0);
System.out.println(girlInfo);
girlCount++;
}
}
System.out.println("随机抽取100万次,其中男生被抽到了" + boyCount);
System.out.println("随机抽取100万次,其中女生被抽到了" + girlCount);
}
}(7) 带权重的随机点名算法-2
TXT文件
钦逸抒-女-21-1.0
屈燕妮-女-24-1.0
阴诗雁-女-25-1.0
伯荷燕-女-24-1.0
欧文新-男-20-1.0
董泽欧-男-18-1.0
滕星磊-男-18-1.0
阚晴岚-女-22-1.0
傅彬远-男-19-1.0
左花依-女-24-1.0Student学生对象
package com.itheima.myiotest6;
public class Student {
private String name;
private String gender;
private int age;
private double weight;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, String gender, int age, double weight) {
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.weight = weight;
}
//get set
public String toString() {
return name + "-" + gender + "-" + age + "-" + weight;
}
}Test测试
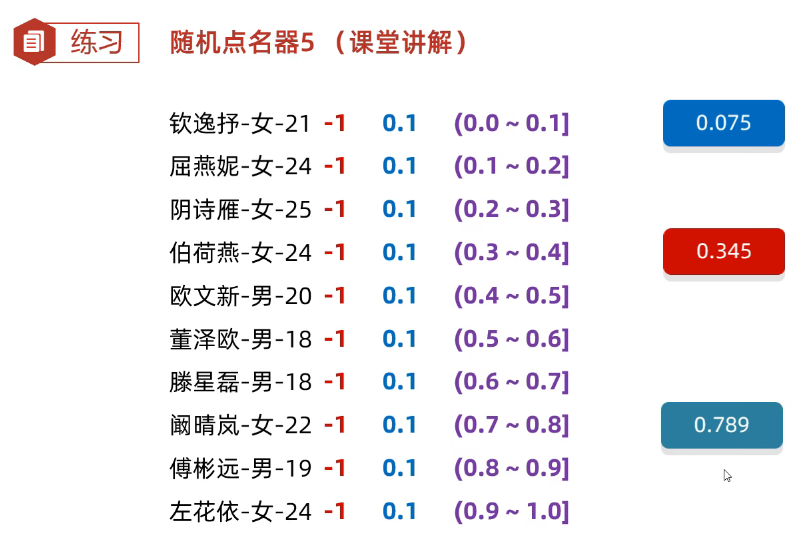
package com.itheima.myiotest6;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.把文件中所有的学生信息读取到内存中
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest6\\names.txt"));
String line;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
String[] arr = line.split("-");
Student stu = new Student(arr[0],arr[1],Integer.parseInt(arr[2]),Double.parseDouble(arr[3]));
list.add(stu);
}
br.close();
//2.计算权重的总和
double weight = 0;
for (Student stu : list) {
weight = weight + stu.getWeight();
}
//3.计算每一个人的实际占比 -- 个人权重 / 总权重
//[0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1, 0.1]
double[] arr = new double[list.size()];
int index = 0;
for (Student stu : list) {
arr[index] = stu.getWeight() / weight;
index++;
}
//4.计算每一个人的权重占比范围
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i] + arr[i - 1];
}
//5.随机抽取
//获取一个0.0~1.0之间的随机数
double number = Math.random();
//判断number在arr中的位置
//二分查找法
//Arrays.binarySearch 该方法会返回:- 插入点 - 1
// - 插入点 - 1 = result
// 插入点 = - result -1
//获取number这个数据在数组当中的插入点位置
int result = - Arrays.binarySearch(arr, number) - 1;
Student stu = list.get(result);
System.out.println(stu);
//6.修改当前学生的权重
double w = stu.getWeight() / 2;
stu.setWeight(w);
//7.把集合中的数据再次写到文件中
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest6\\names.txt"));
for (Student s : list) {
bw.write(s.toString());
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}4、登录注册
(1)登录验证
userInfo文件
username=zhangsan&password=123测试
package com.itheima.myiotest7;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:写一个登陆小案例。
步骤:
将正确的用户名和密码手动保存在本地的userinfo.txt文件中。
保存格式为:username=zhangsan&password=123
让用户键盘录入用户名和密码
比较用户录入的和正确的用户名密码是否一致
如果一致则打印登陆成功
如果不一致则打印登陆失败
*/
//1.读取正确的用户名和密码
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest7\\userinfo.txt"));
String line = br.readLine();//username=zhangsan&password=123
br.close();
String[] userInfo = line.split("&");
String[] arr1 = userInfo[0].split("=");
String[] arr2 = userInfo[1].split("=");
String rightUsername = arr1[1];
String rightPassword = arr2[1];
//2.用户键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//3.比较
if(rightUsername.equals(username) && rightPassword.equals(password)){
System.out.println("登陆成功");
}else{
System.out.println("登陆失败");
}
}
}(2)登录验证-次数限制
userInfo文件
username=zhangsan&password=123&count=4测试
package com.itheima.myiotest8;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
需求:写一个登陆小案例(添加锁定账号功能)
步骤:
将正确的用户名和密码手动保存在本地的userinfo.txt文件中。
保存格式为:username=zhangsan&password=123&count=0
让用户键盘录入用户名和密码
比较用户录入的和正确的用户名密码是否一致
如果一致则打印登陆成功
如果不一致则打印登陆失败,连续输错三次被锁定
*/
//1.读取正确的用户名和密码
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest8\\userinfo.txt"));
String line = br.readLine();//username=zhangsan&password=123&count=0
br.close();
String[] userInfo = line.split("&");
String[] arr1 = userInfo[0].split("=");
String[] arr2 = userInfo[1].split("=");
String[] arr3 = userInfo[2].split("=");
String rightUsername = arr1[1];
String rightPassword = arr2[1];
//count:表示用户连续输错的次数
int count = Integer.parseInt(arr3[1]);
//2.用户键盘录入用户名和密码
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入用户名");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码");
String password = sc.nextLine();
//3.比较
if (rightUsername.equals(username) && rightPassword.equals(password) && count < 3) {
System.out.println("登陆成功");
writeInfo("username=" + rightUsername + "&password=" + rightPassword + "&count=0");
} else {
count++;
if (count < 3) {
System.out.println("登陆失败,还剩下" + (3 - count) + "次机会");
} else {
System.out.println("用户账户被锁定");
}
writeInfo("username=" + rightUsername + "&password=" + rightPassword + "&count=" + count);
}
}
/*
* 作用:
* 写出一个字符串到本地文件中
* 参数:
* 要写出的字符串
* */
public static void writeInfo(String content) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myiotest\\src\\com\\itheima\\myiotest8\\userinfo.txt"));
bw.write(content);
bw.close();
}
}二十、Properties-配置的基本使用
更新: 2025/4/9 字数: 0 字 时长: 0 分钟
1、配置文件

2、Properties的体系-Map
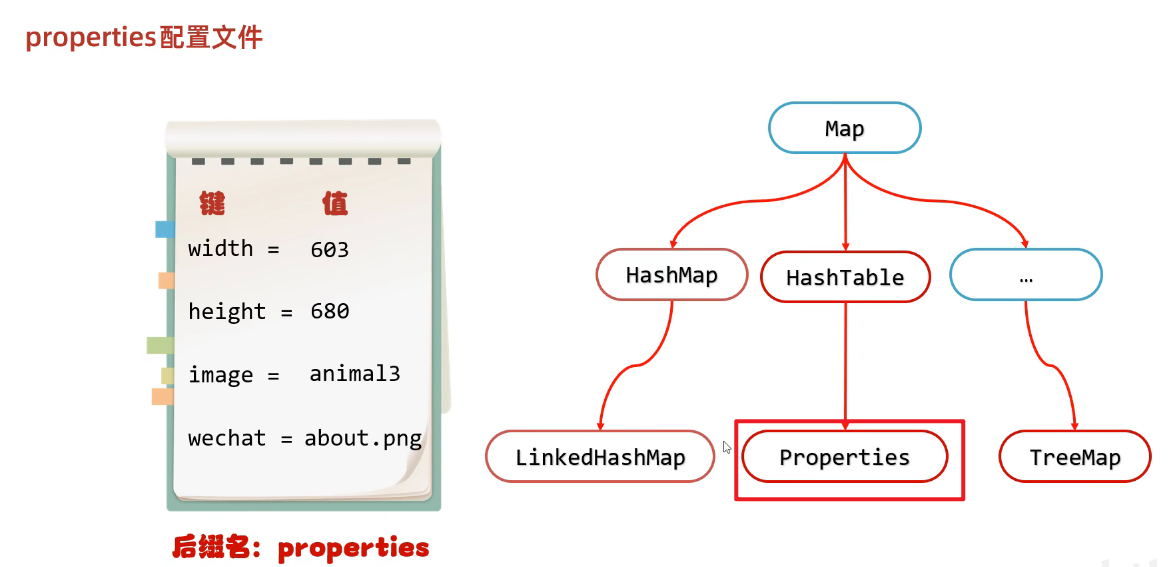

3、示例代码
(1)Properties作为Map集合的操作
package com.itheima.myiotest9;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Properties作为Map集合的操作
*/
//1.创建集合的对象
Properties prop = new Properties();
//2.添加数据
//细节:虽然我们可以往Properties当中添加任意的数据类型,但是一般只会往里面添加字符串类型的数据
prop.put("aaa","111");
prop.put("bbb","222");
prop.put("ccc","333");
prop.put("ddd","444");
//3.遍历集合
/*Set<Object> keys = prop.keySet();
for (Object key : keys) {
Object value = prop.get(key);
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}*/
/* Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> entries = prop.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entries) {
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + "=" + value);
}*/
}
}(2)写入Properties配置文件-store
package com.itheima.myiotest9;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
/*
Properties跟IO流结合的操作
*/
//1.创建集合
Properties prop = new Properties();
//2.添加数据
prop.put("aaa","bbb");
prop.put("bbb","ccc");
prop.put("ddd","eee");
prop.put("fff","iii");
//3.把集合中的数据以键值对的形式写到本地文件当中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("myiotest\\a.properties");
prop.store(fos,"test");
fos.close();
/*BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myiotest\\a.properties"));
Set<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> entries = prop.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entries) {
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object value = entry.getValue();
bw.write(key + "=" + value);
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();*/
}
}(3)加载Properties配置文件-load
package com.itheima.myiotest9;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建集合
Properties prop = new Properties();
//2.读取本地Properties文件里面的数据
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("myiotest\\a.properties");
prop.load(fis);
fis.close();
//3.打印集合
System.out.println(prop);
}
}